Enterprise Variables Data
Overview
Enterprise Variables Data provides access to all Enterprise Variables (EVs) defined in the AI Command Center. Enterprise Variables are shared configuration values that can be reused across workflows, agents, and projects within the same tenant.
Unlike Model Data, which is scoped to a single workflow instance, Enterprise Variables are:
- Centrally managed
- Tenant-scoped
- Designed for cross-process reuse
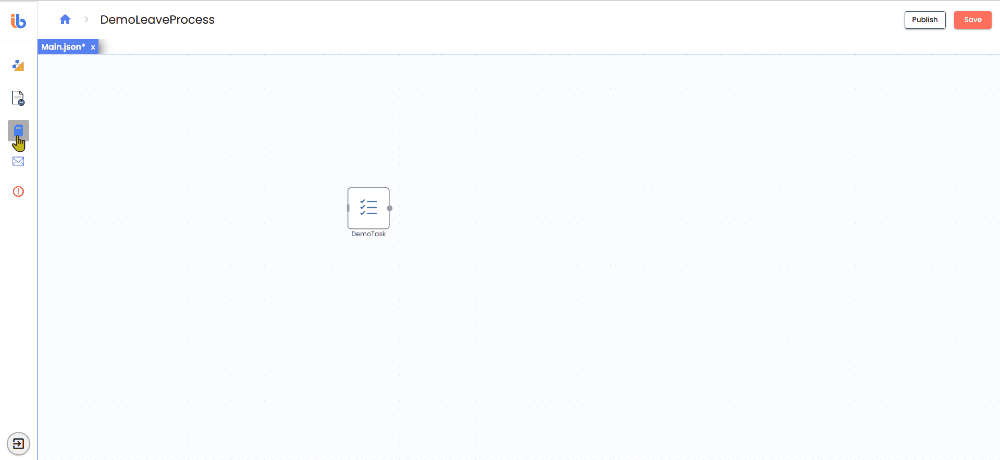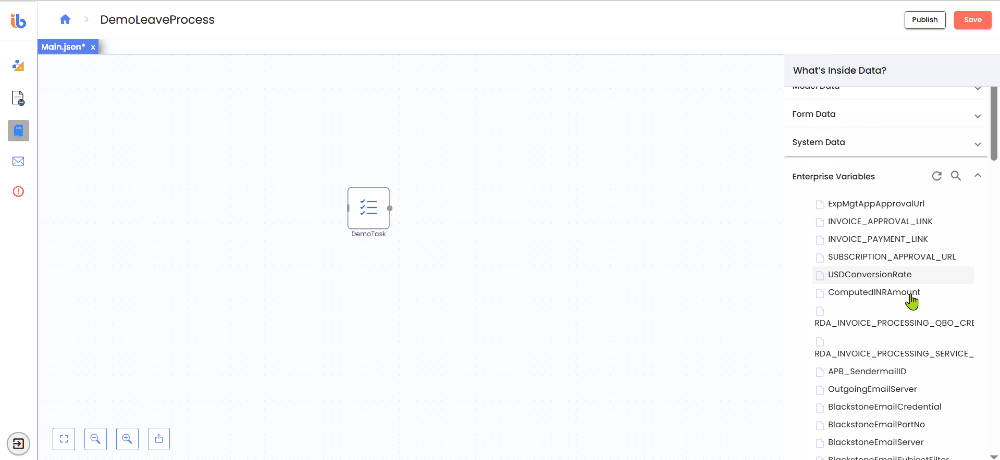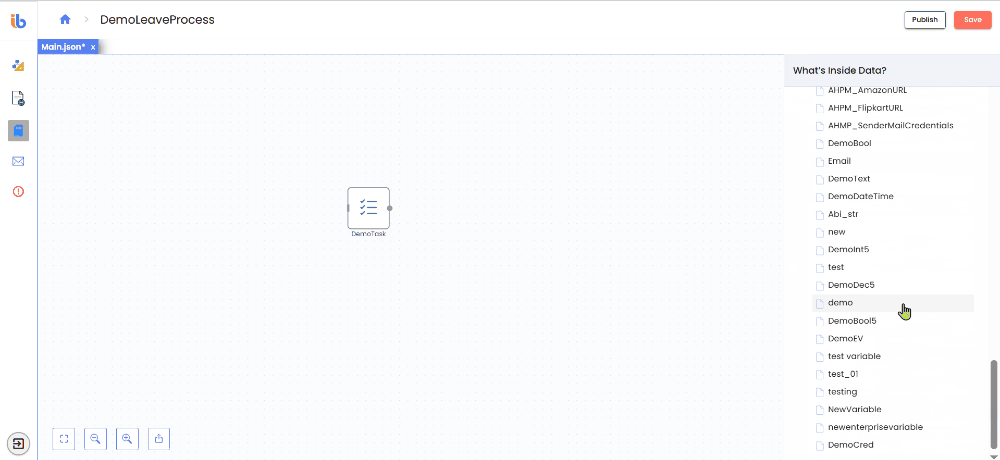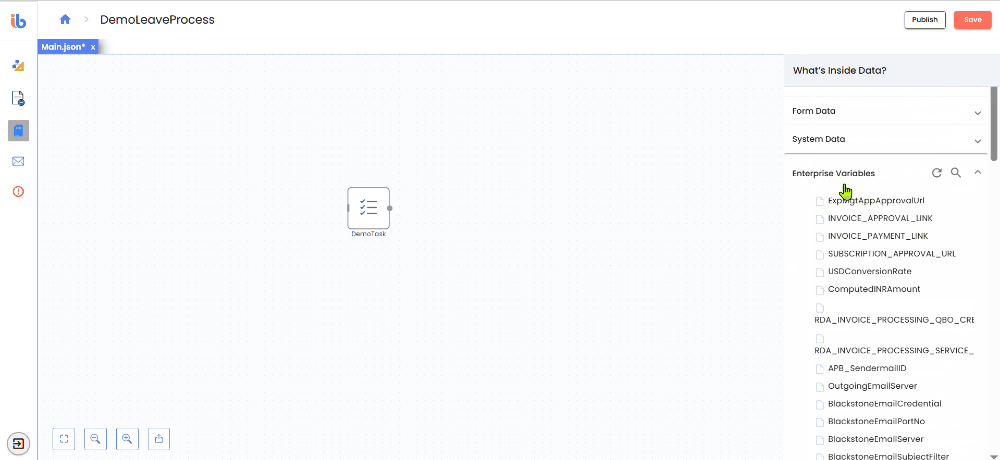
What are Enterprise Variables?
Enterprise Variables store values that need to be:
- Shared across multiple workflows or agents
- Centrally governed by administrators
- Reused without redefining them in each workflow
Common examples include:
- Environment-specific URLs or endpoints
- Feature flags and configuration switches
- Thresholds and limits
- Credentials and sensitive configuration values
- Shared reference or lookup values
Scope of Enterprise Variables
Enterprise Variables are always tenant-scoped, and each variable can additionally be defined with one of the following scopes at creation time:
| Scope | Description |
|---|---|
| Global | The variable is available to all users and all workflows within the tenant. |
| User | The variable is available only to the specific user within the tenant and is not visible to other users or workflows executed by them. |
This scoping mechanism allows organizations to balance shared configuration with user-specific values where required.
Encrypted Enterprise Variables (Secure Storage)
Enterprise Variables can be marked as Encrypted at definition time.
When encryption is enabled:
- The variable value is stored encrypted at rest
- The value is never displayed in plain text
- The variable behaves like a secure vault entry for sensitive information
Encrypted Enterprise Variables are typically used to store:
- Passwords
- API keys
- Tokens
- Secrets and credentials
At runtime, encrypted values are securely decrypted in memory and made available only to authorized workflows and activities.
Using Enterprise Variables in Workflows
Enterprise Variables can be:
- Referenced as inputs to activities
- Used in conditions and expressions
- Read during workflow execution
- Accessed consistently across workflows based on their defined scope and encryption settings
Enterprise Variables are read-only within the workflow designer. Creation, modification, encryption settings, or deletion must be performed from the AI Command Center.
Behavior and Resolution
- Enterprise Variables are resolved at runtime
- Scope rules (Global or User) are enforced automatically
- Encryption is transparent to workflows at execution time
- Changes to a Global Enterprise Variable affect all workflows that reference it
- Changes to a User-scoped Enterprise Variable affect only workflows executed by that user
- Type safety is enforced when binding Enterprise Variables to activity inputs
When to Use Enterprise Variables vs Model Data
| Use Case | Recommended Data Type |
|---|---|
| Workflow-specific business data | Model Data |
| Per-instance values | Model Data |
| Shared tenant-wide configuration | Enterprise Variables (Global) |
| User-specific configuration | Enterprise Variables (User) |
| Credentials and secrets | Enterprise Variables (Encrypted) |
| Administrator-managed values | Enterprise Variables |
Best Practices
- Use Global Enterprise Variables for shared configuration
- Use User Enterprise Variables for user-specific preferences
- Enable Encryption for all sensitive values
- Avoid storing frequently changing runtime data as Enterprise Variables
- Use clear, descriptive names to simplify governance and auditing
- Review scope and encryption settings carefully during creation
Enterprise Variables provide a secure, centralized, and flexible mechanism for managing shared and sensitive configuration across automation solutions.