Azure Active Directory
Introduction
This page describes how to configure Azure Active Directory (Azure AD) as an authentication provider for the AI Command Center. Azure AD authentication allows organizations to integrate cloud-based identity management and support multiple Azure AD tenants within a single AI Command Center instance.
Overview
Using the Azure Active Directory authentication provider, you can:
- Register and manage multiple Azure Active Directory providers
- Enable or disable providers without losing their configuration
- Configure independent user and group synchronization schedules for each Azure AD provider
- Allow users to authenticate using any registered Azure Active Directory
This enhancement extends the existing authentication framework by introducing Azure Active Directory as a supported authentication type alongside Local Active Directory.
Configuration flow
Follow the steps below to configure Azure Active Directory as an authentication provider:
1) Basic Information
Provide basic details to identify and manage the authentication provider:
- Provider Name – Enter a unique name for this Azure AD configuration.
- Description – Enter a brief description of the provider.
- Enabled – Turn the provider on or off without removing its configuration.
2) Azure AD Settings
- Connect To Azure AD – Click this option to initiate Microsoft admin consent. After consent is granted, the system automatically populates the Tenant ID and Organization Name.
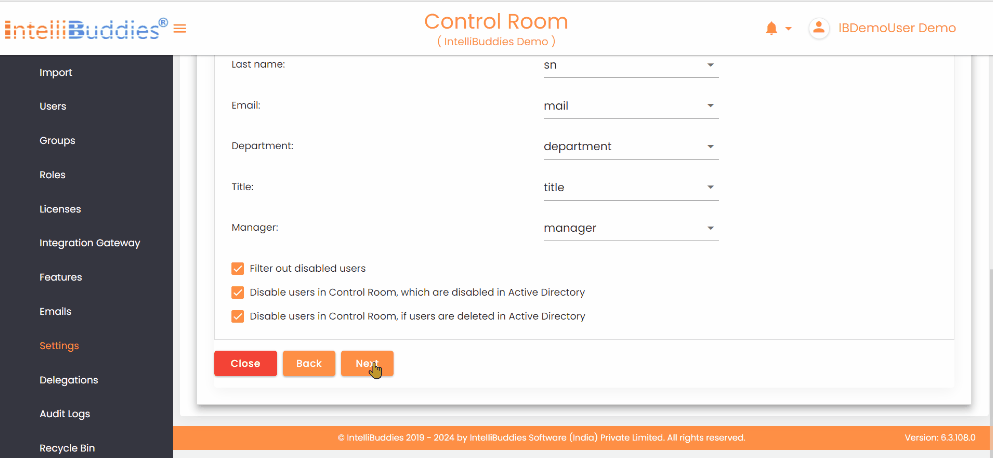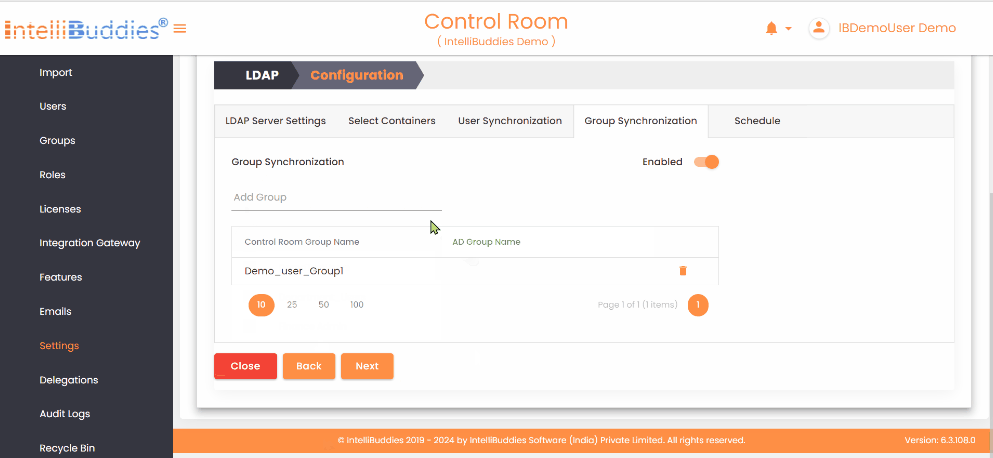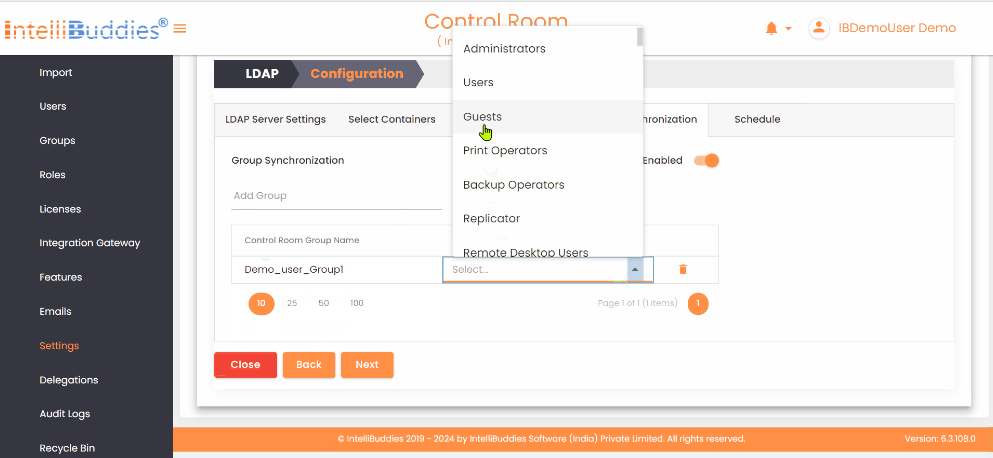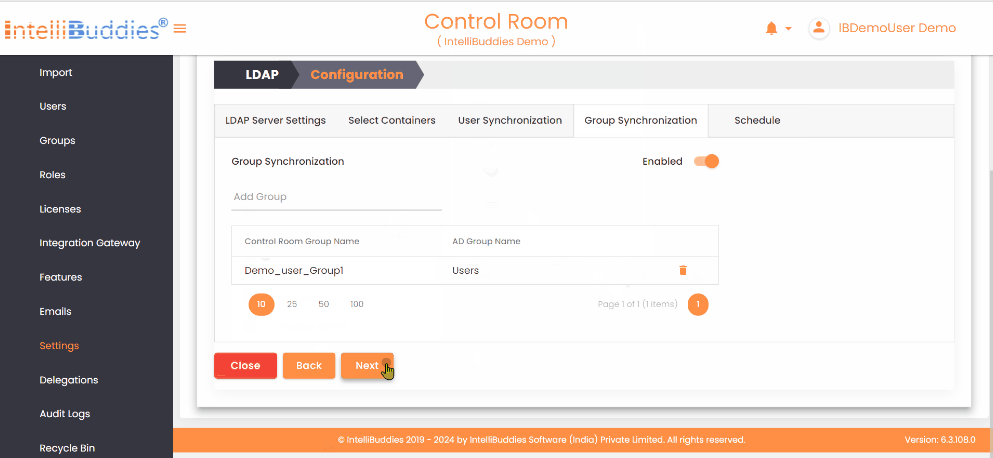
3) User Synchronization
Configure how users synchronize from Azure Active Directory into the AI Command Center:
- Map user attributes such as: - Account Name - First/Last Name - Email - Department - Title - Manager
- The system suggests default mappings automatically. Modify these only if you use custom attributes.
- Defaults are suggested automatically; adjust only for custom attributes Synchronization Options: - Filter out disabled users - Disable AI Command Center users when Azure AD users are disabled - Disable AI Command Center users when Azure AD users are deleted
| Options | Description |
|---|---|
Filter out disabled users | Excludes disabled users from Azure Active Directory during synchronization. |
Disable users in Control Room, which are disabled in Active Directory | Automatically disables Control Room users when they are disabled in Azure Active Directory. |
Disable users in Control Room, if users are deleted in Active Directory | Automatically disables Control Room users when they are deleted from Azure Active Directory. |
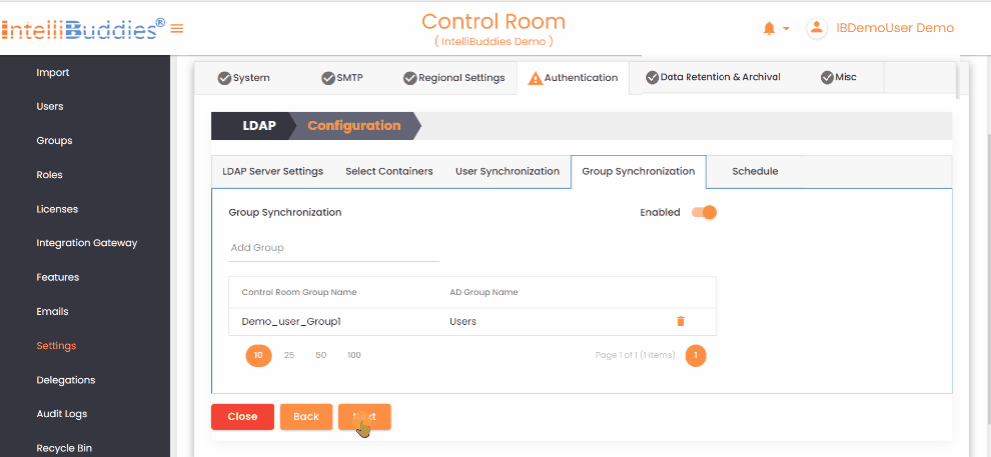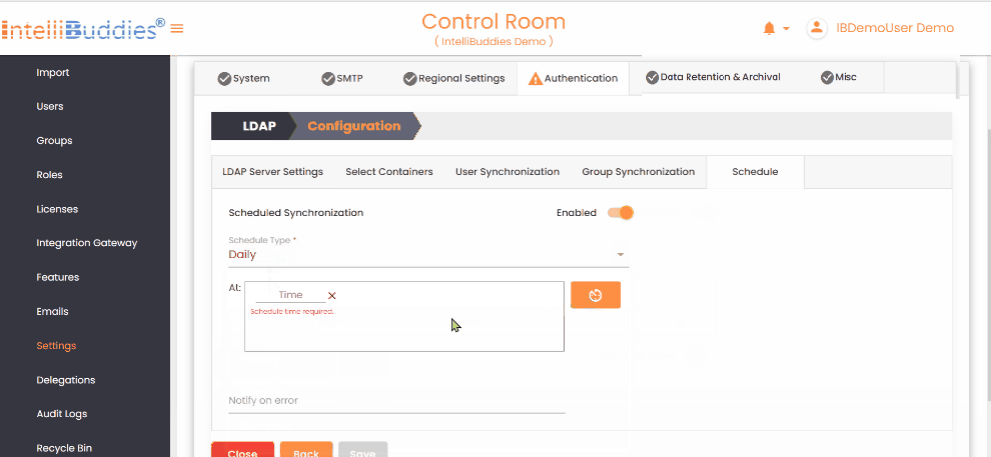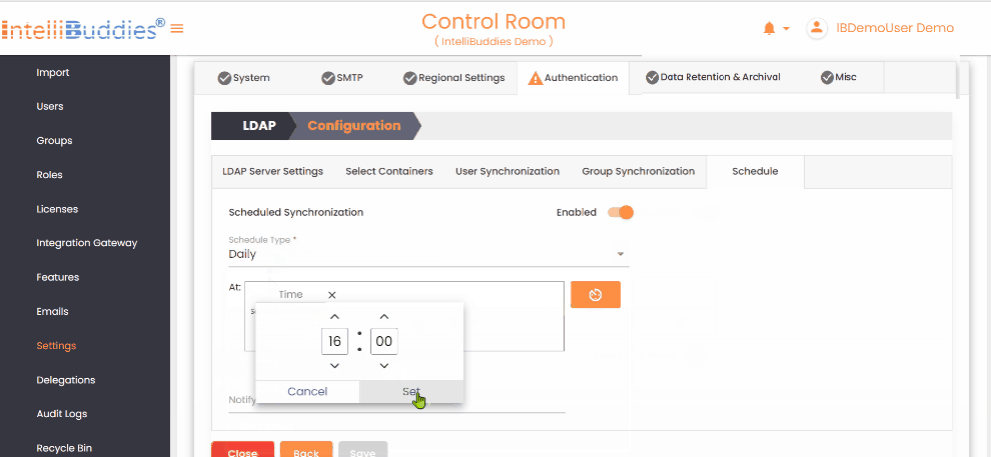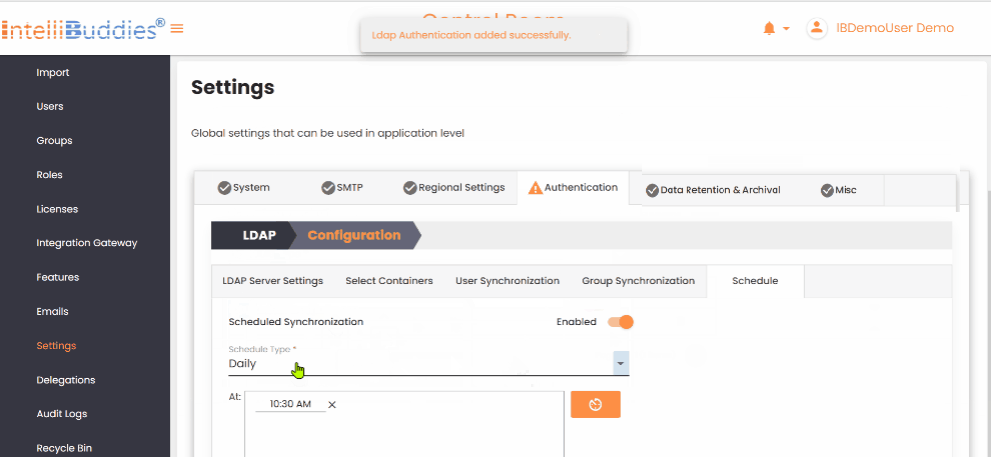
4) Group Synchronization
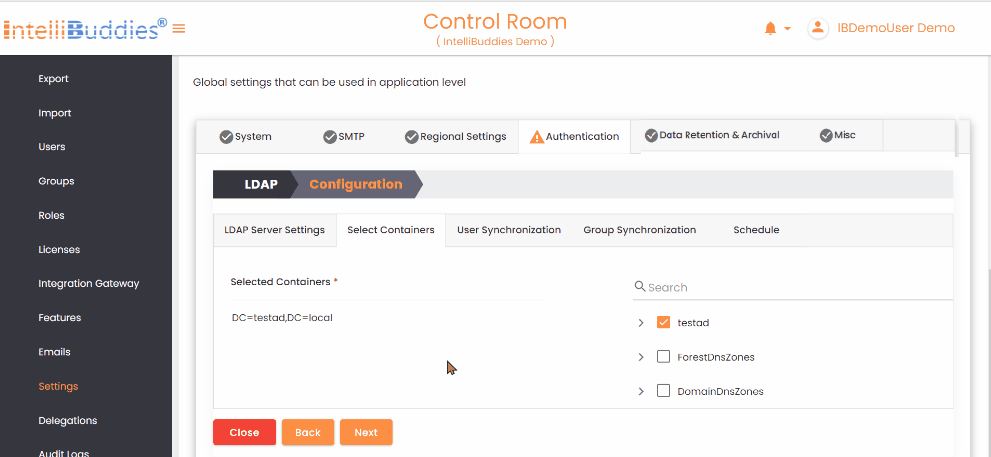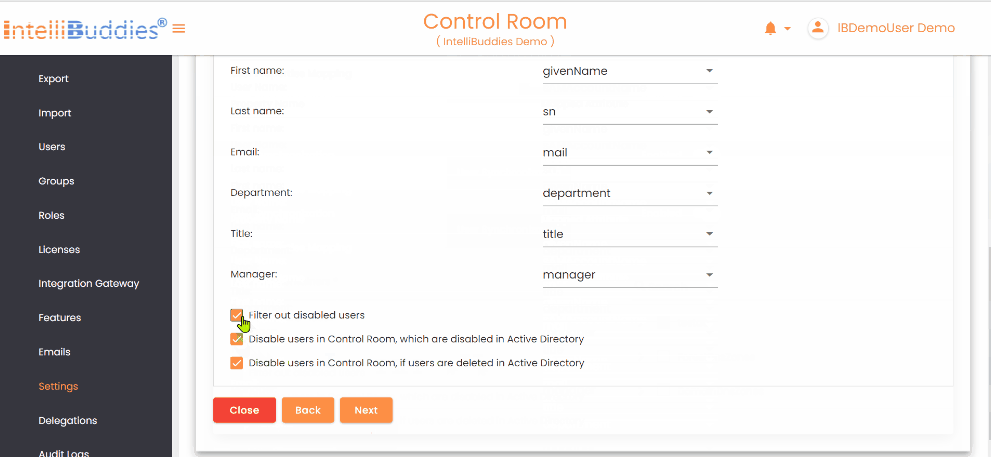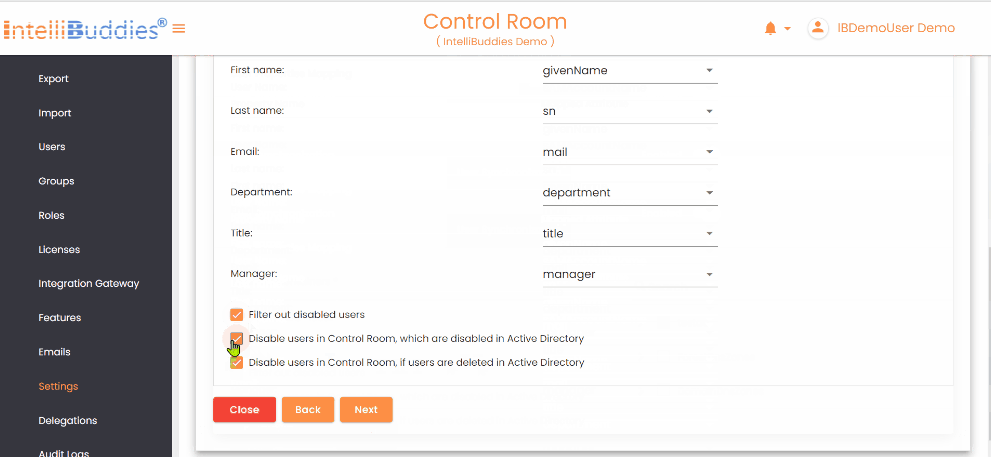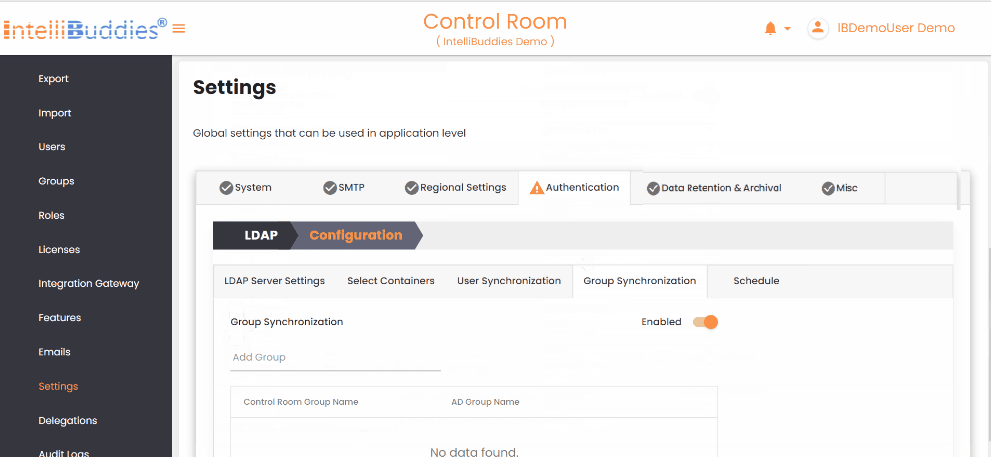
To synchronize groups: - Create the required groups in the AI Command Center. - Map each AI Command Center group to its corresponding Azure Active Directory group in the Group Synchronization tab. The system synchronizes only mapped groups and reflects any membership changes from Azure Active Directory in the corresponding AI Command Center groups.
5) Schedule User and Group Synchronization
Configure periodic synchronization in the Schedule tab. Set up periodic User and Group synchronization in the Schedule tab.
- Select the appropriate Schedule Types
- Specify Notify To email addresses to receive error notifications.
6) Review & Save
Review the configuration and save your changes:
- The system creates or updates the authentication provider.
- Existing credentials remain unchanged unless you explicitly update them.
Required Microsoft Graph API permissions
| Permission Name | Description |
|---|---|
| User.Read.All | Read all users |
| Group.Read.All | Read all groups |
| organization.Read.All | Read organization information |
| openid | Sign users in |
| profile | View users' basic profile |
| offline_access | Maintain access to granted data |
Single Sign-On
- After licensing and configuration, the Login page displays an Azure AD button.
- Clicking this button redirects users to the Microsoft sign-in page to authenticate using Azure Active Directory.