Triggers
Triggers enable you to execute your Automation based on specific criteria. You can run Automation on an ad-hoc basis, but if you want to pre-plan your executions, you can configure a particular trigger.
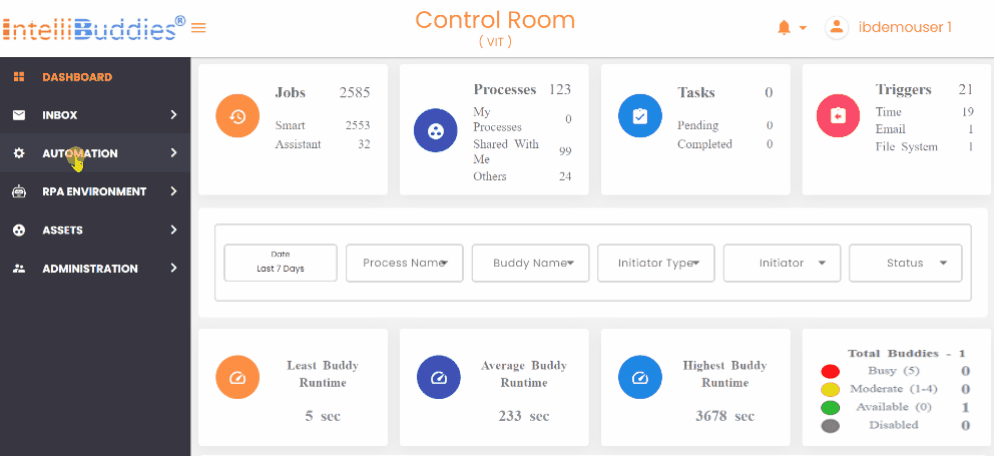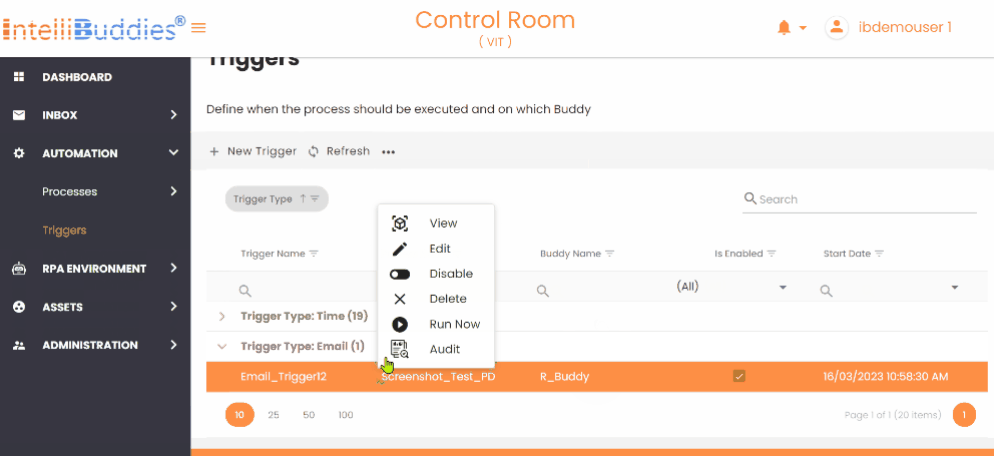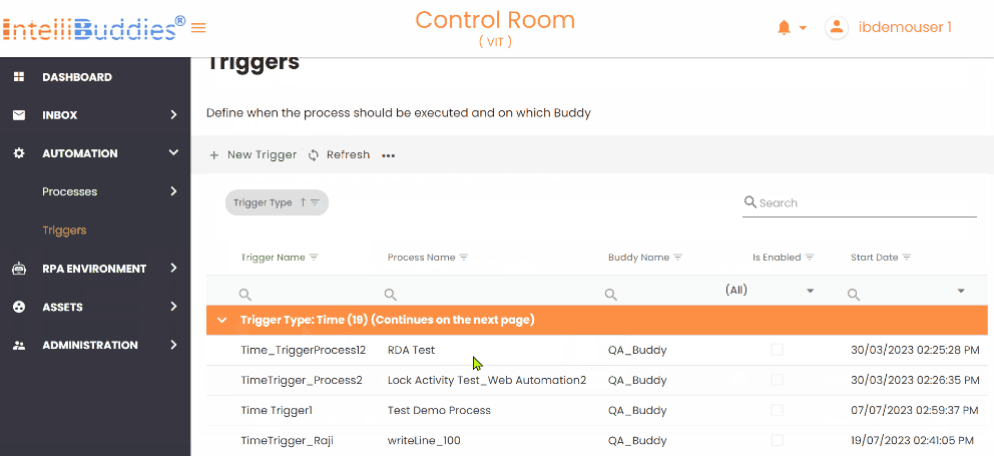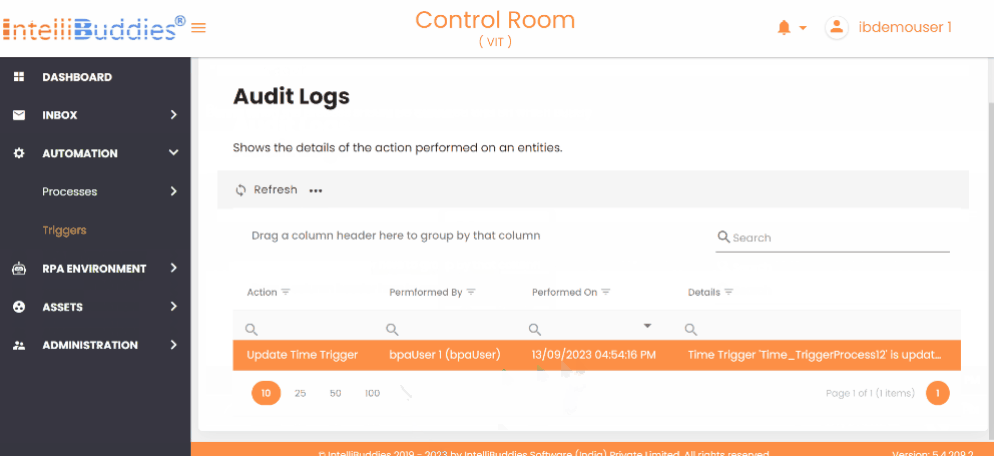
Context Menu Options
You can manage automation triggers from the Triggers page in AI Command Center, provided you have the appropriate permissions.
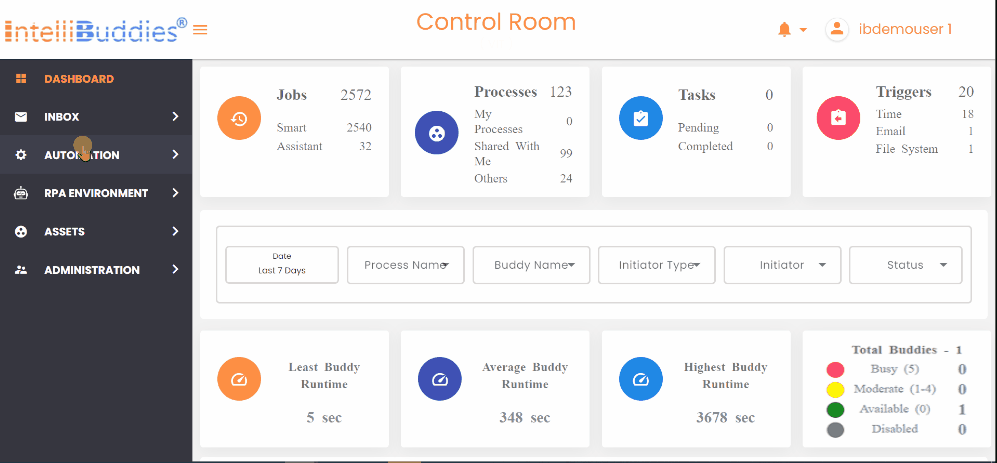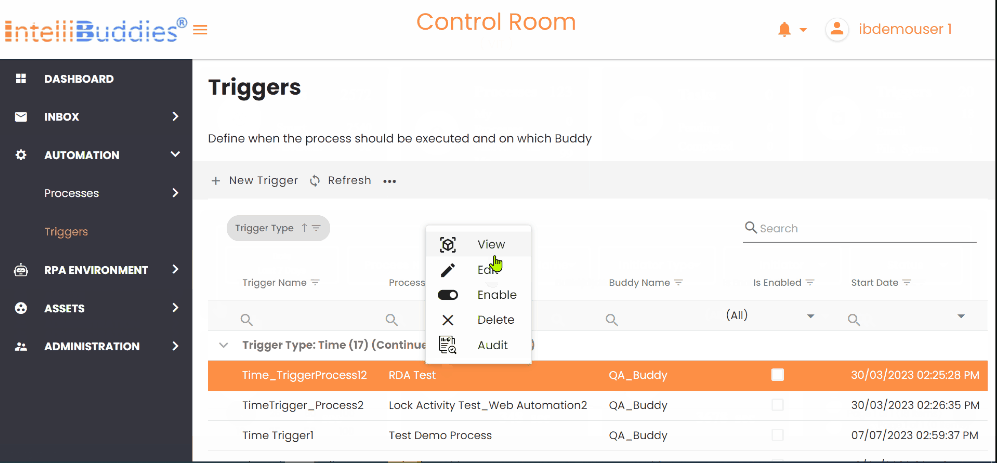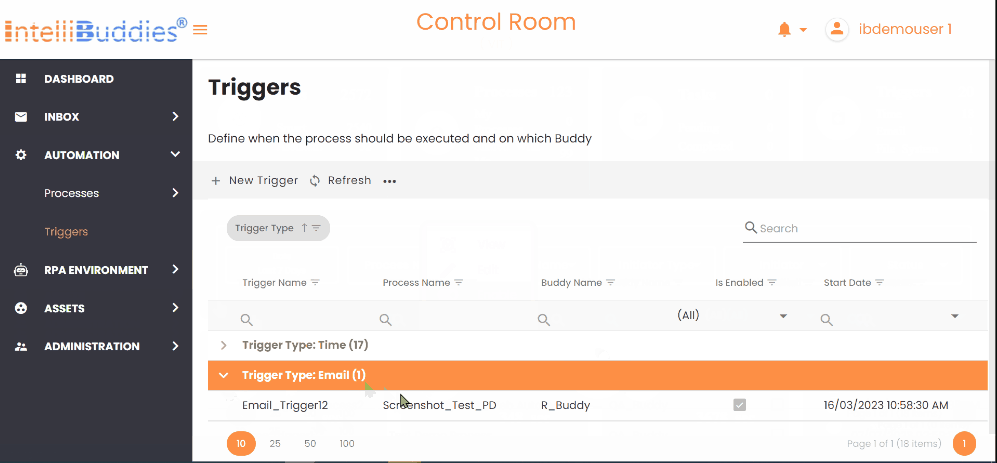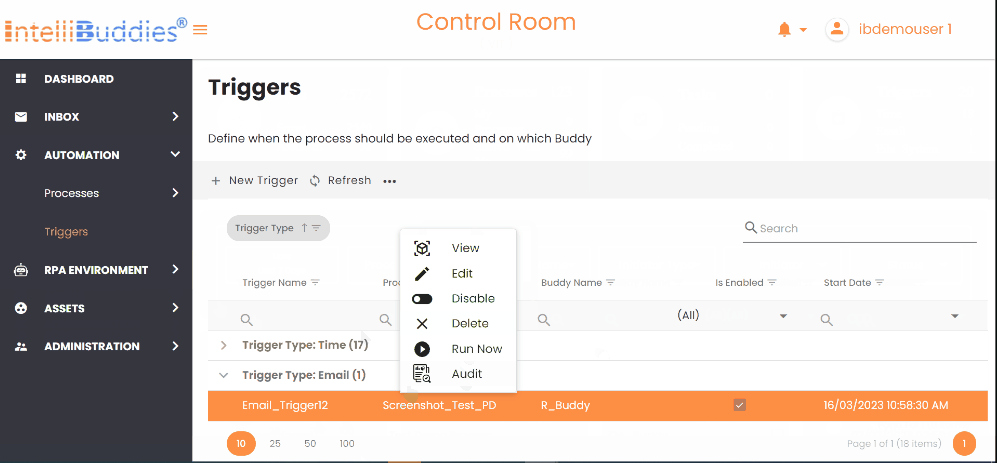
| Permission | Description |
|---|---|
| View | View all Triggers and their details |
| Edit | Edit Trigger details |
| Delete | Delete a Trigger |
| Enable/Disable | Enable/Disable a Trigger by clicking on this option |
| RunNow | This option is shown only for Email Triggers. Select this option to manually activate Email Triggers and verify for new incoming emails. |
| Audit | You can audit the operations on Trigger |
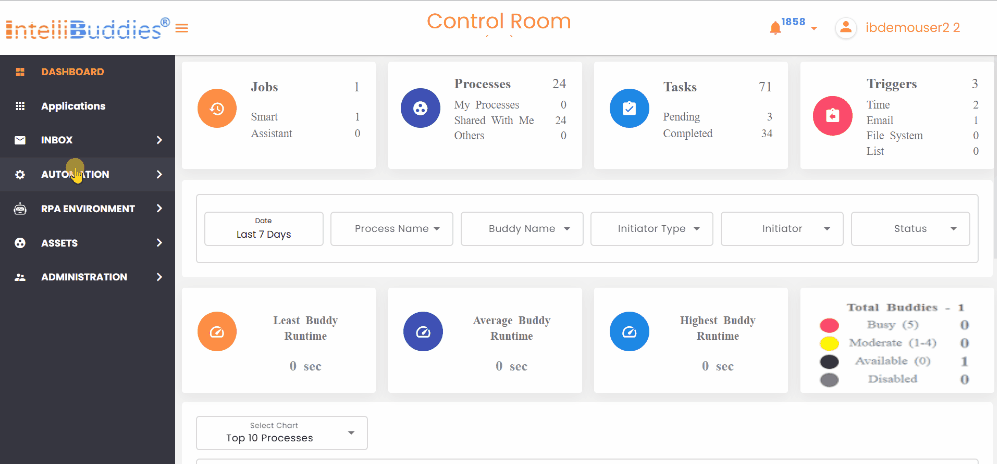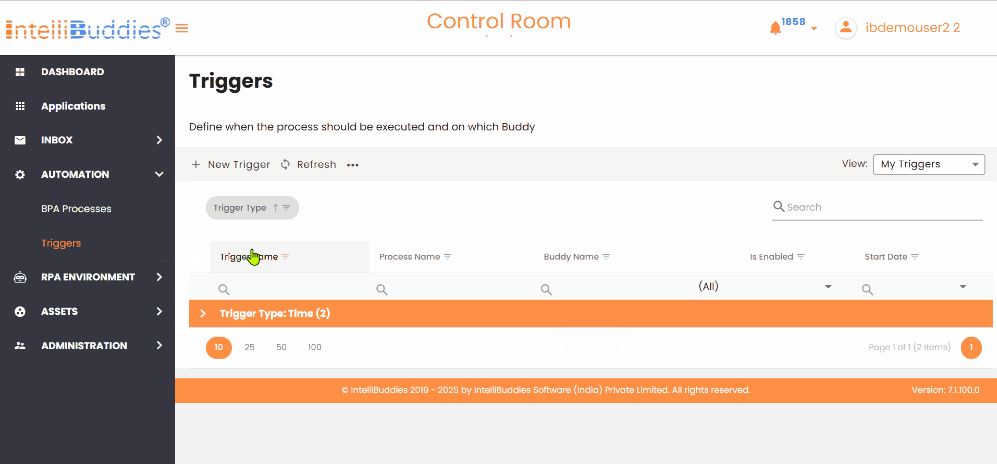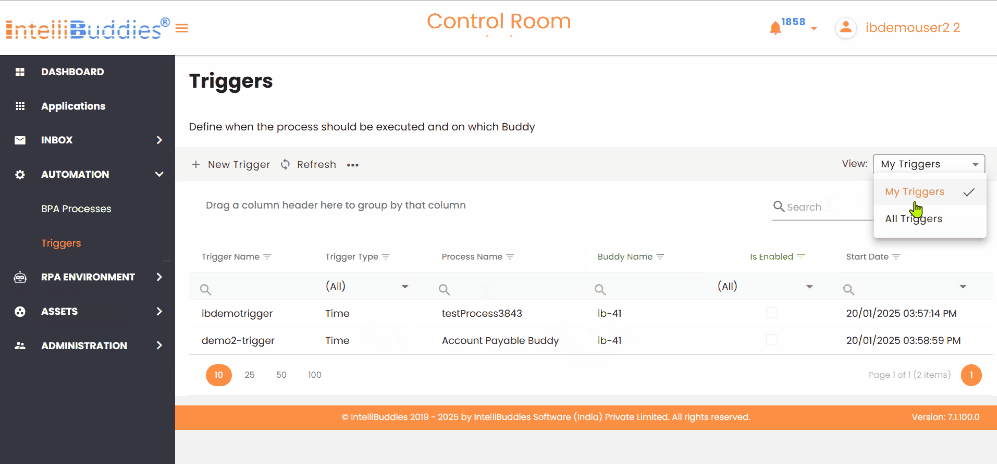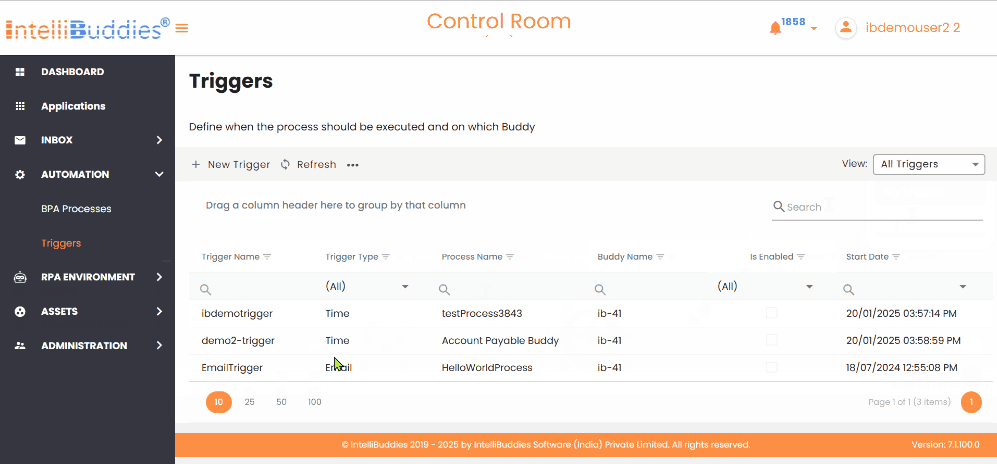
Triggers View
You can change the display view on the Triggers page in the AI Command Center by selecting View from the Context Menu. The available viewing options are as follows:
| View | Description |
|---|---|
| My Triggers | Displays only the triggers the currently logged-in user created. It is the default view. |
| All Triggers | Displays all triggers available in the system, including those created by other users. |
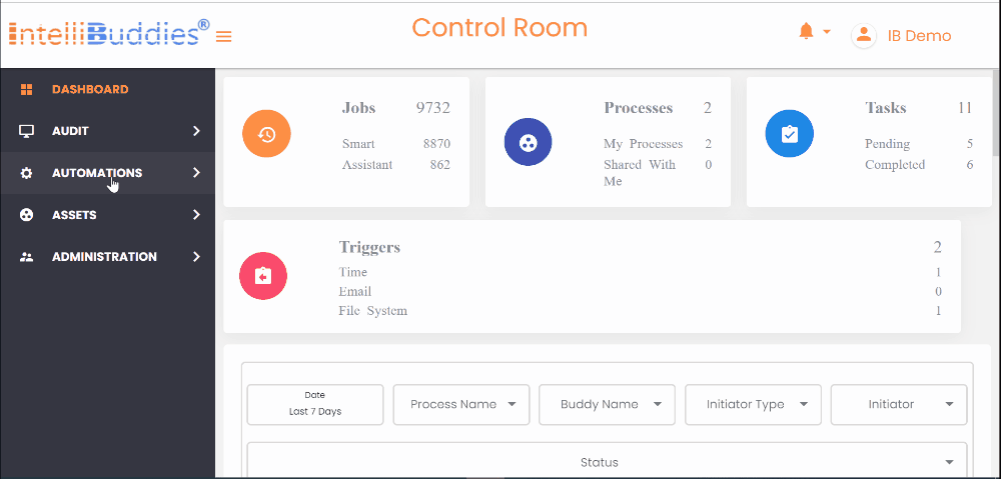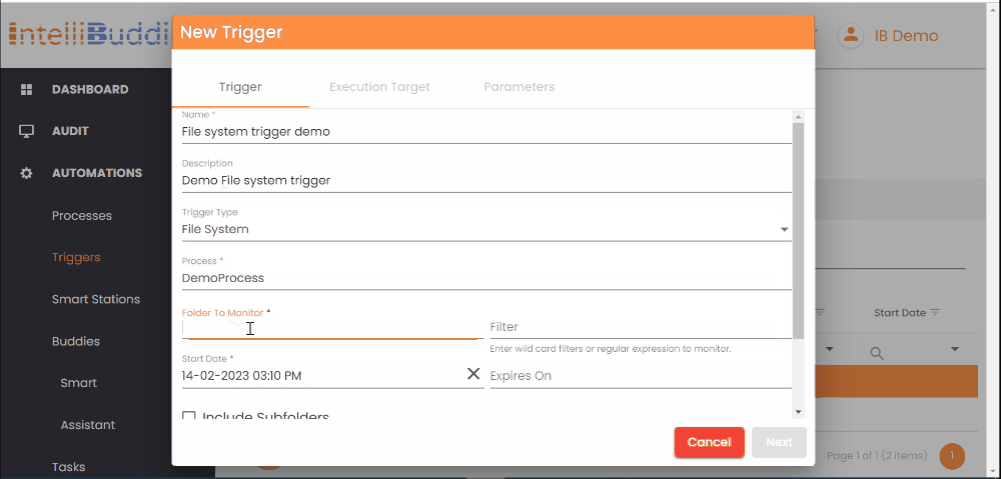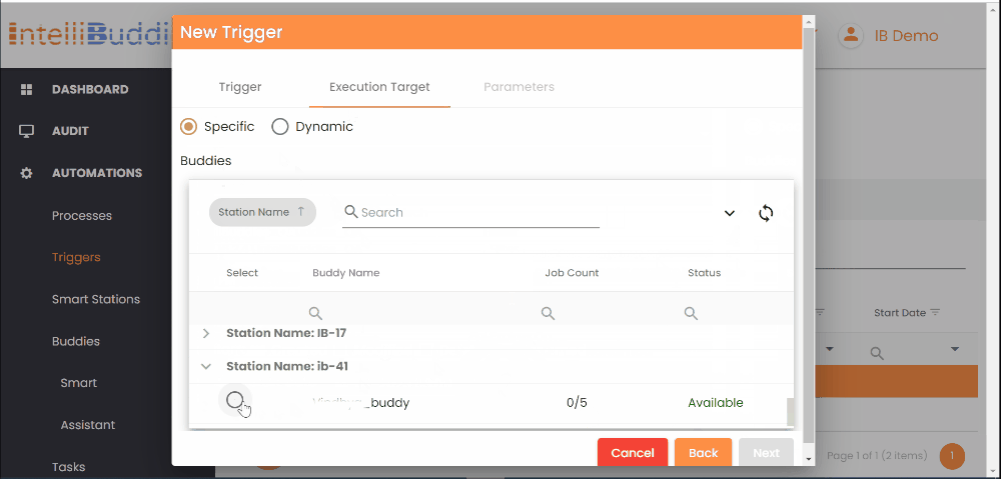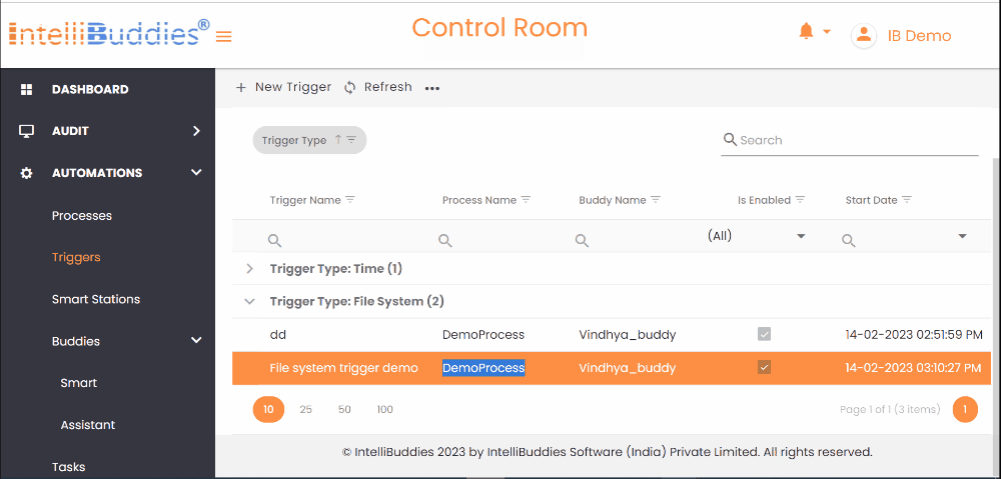
Creating a Trigger
You can create a new Trigger from AI Command Center > Triggers page.
- Click on Toolbar-Menu >
button
- New Trigger dialog appears.
- Fill in the required trigger information by following the instructions mentioned in Trigger Tab, Execution Tab, and Parameter Tab.
Trigger Tab
- Enter a name for the trigger for easy identification.
- Choose a Process that you want to execute
- Select the Trigger Type from the dropdown
- Fill in the trigger criteria based on the type selected: Time Trigger Criteria | Email Trigger Criteria | File System Trigger Criteria
- Optionally, specify the trigger Start Date. By default, the trigger is initiated immediately after creation.
- Optionally, specify the trigger Expiry Date. If specified, it will stop triggering new jobs after this date. By default, the trigger will never expire.
Execution Target Tab
- Select the specific Smart Buddy that should execute the process.
If you select the Dynamic option, any of the available Smart Buddy will pick up the job for execution
Parameters Tab
- Specify the Log Level for the job executed with this Trigger.
- To submit the necessary input parameters for a selected process, bind them according to the type of trigger chosen. You can find instructions on how to bind Email Trigger Parameters and File System Trigger Parameters by following these links: Binding Email Trigger Parameters | Binding File System Trigger Parameters.
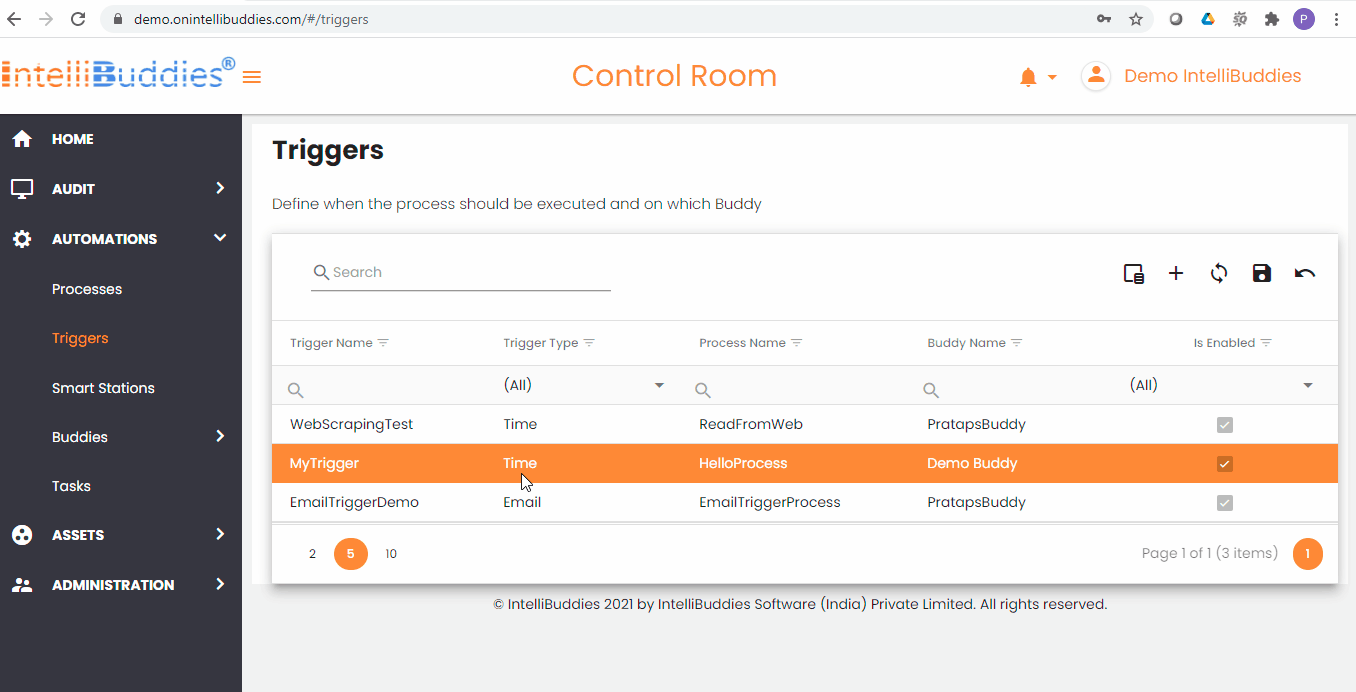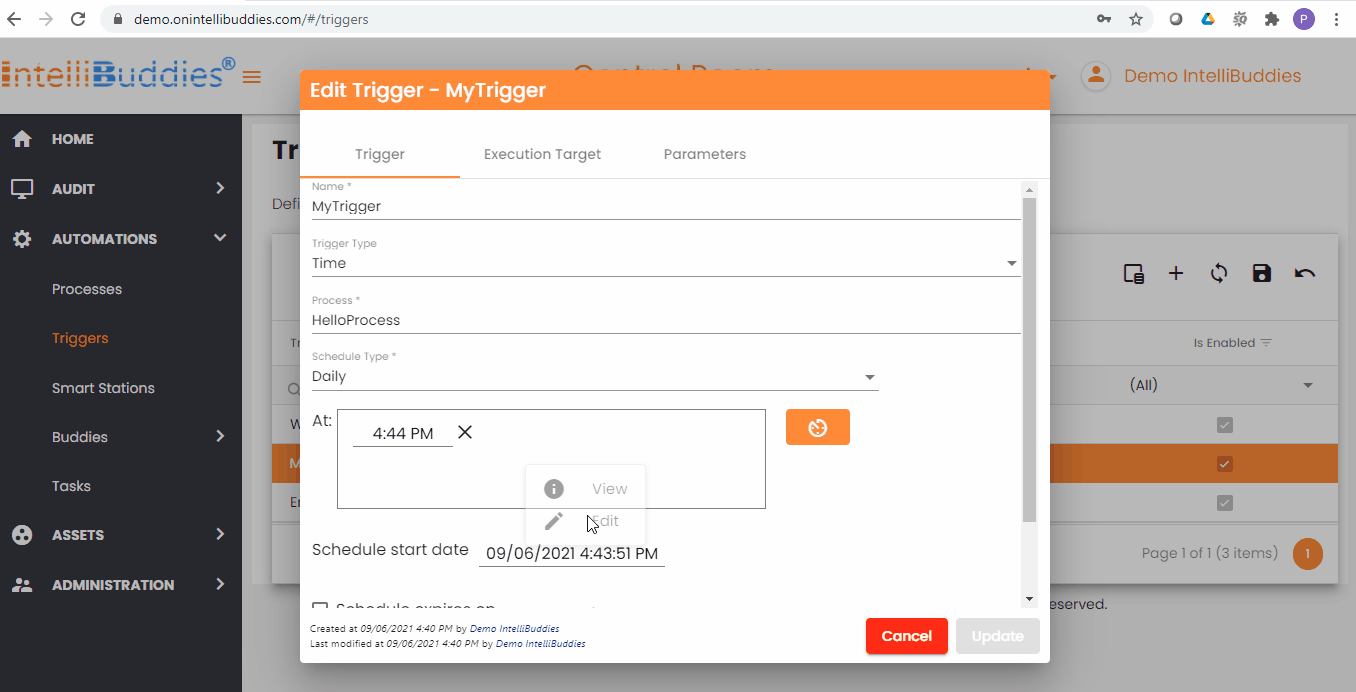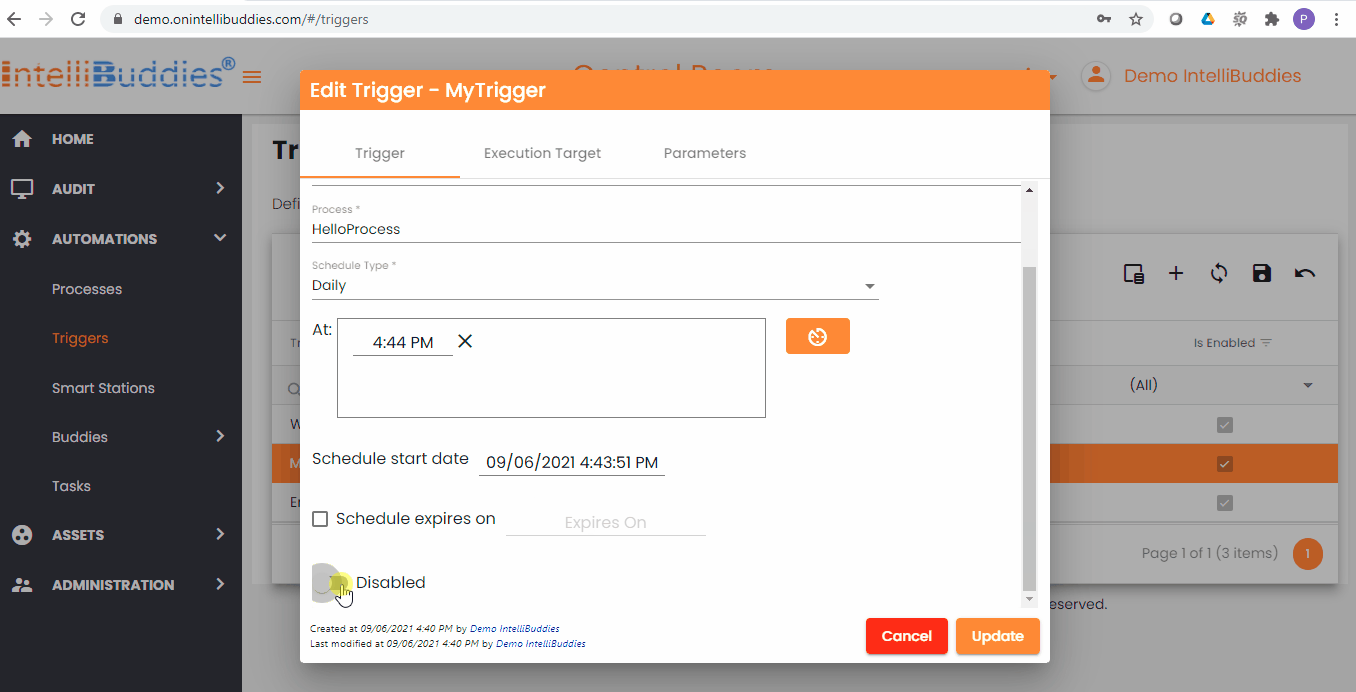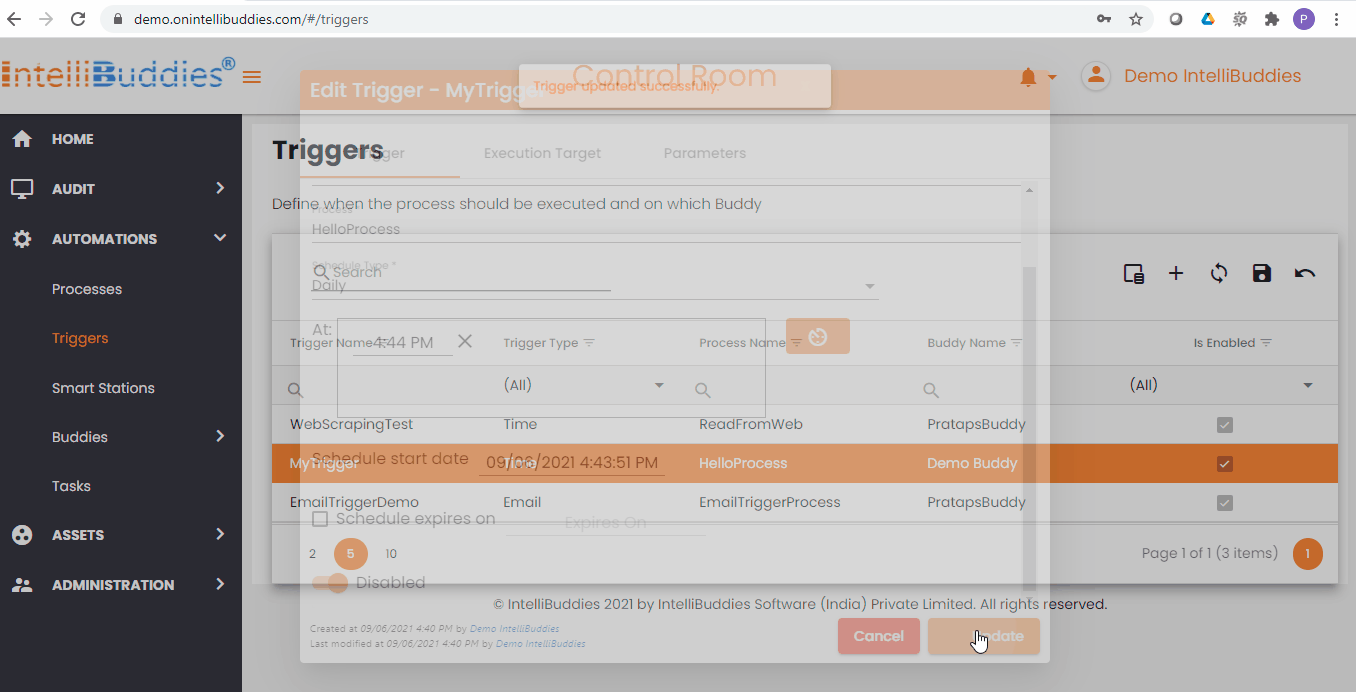
Updating a Trigger
You can update an existing trigger to change the details. You can do this from the Triggers page
- Select a trigger to update
- Select from Context-Menu > Edit option
- Update the details
- Click on Update
Deleting a Trigger
- On the Triggers page, select the trigger you want to delete.
- Right-click to open the context menu, then click Delete.
- Confirm the prompt to permanently delete the selected trigger.
A user with the Administrator role can delete an existing Trigger.
Enabling/Disabling a Trigger
- On the Triggers page, select the trigger you want to enable or disable.
- Right-click to open the context menu, then choose Enable or Disable.
- The trigger's status updates accordingly.
- The selected trigger will be enabled or disabled accordingly.
- You can verify the status in the Is Enabled column; a checked box indicates that the trigger is enabled.
- Disabling a Trigger will block the execution of Automation.
- Turn off the Disable button to enable the trigger.
- When you delete a process, all associated triggers are automatically disabled. To restore functionality, users must manually reconfigure triggers upon re-adding the process.
Audit a Trigger
- On the Triggers page, select the trigger you want to audit.
- Right-click to open the Context Menu and select Audit.
- This opens the Audit Logs page, displaying a history of actions performed on the selected trigger.
Trigger Types
IntelliBuddies supports the following types of Triggers:
| Trigger Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Time | Schedule a job to run at a specific time according to predetermined criteria. |
| Invokes a job when a new email arrives on the specified email box and matches the specified criteria. | |
| File System | Invokes a job when a specified file event(s) occur under the specified folder(s) |
| List | Invokes a job on data inserted/updated/deleted inside a List matches the specified criteria. |
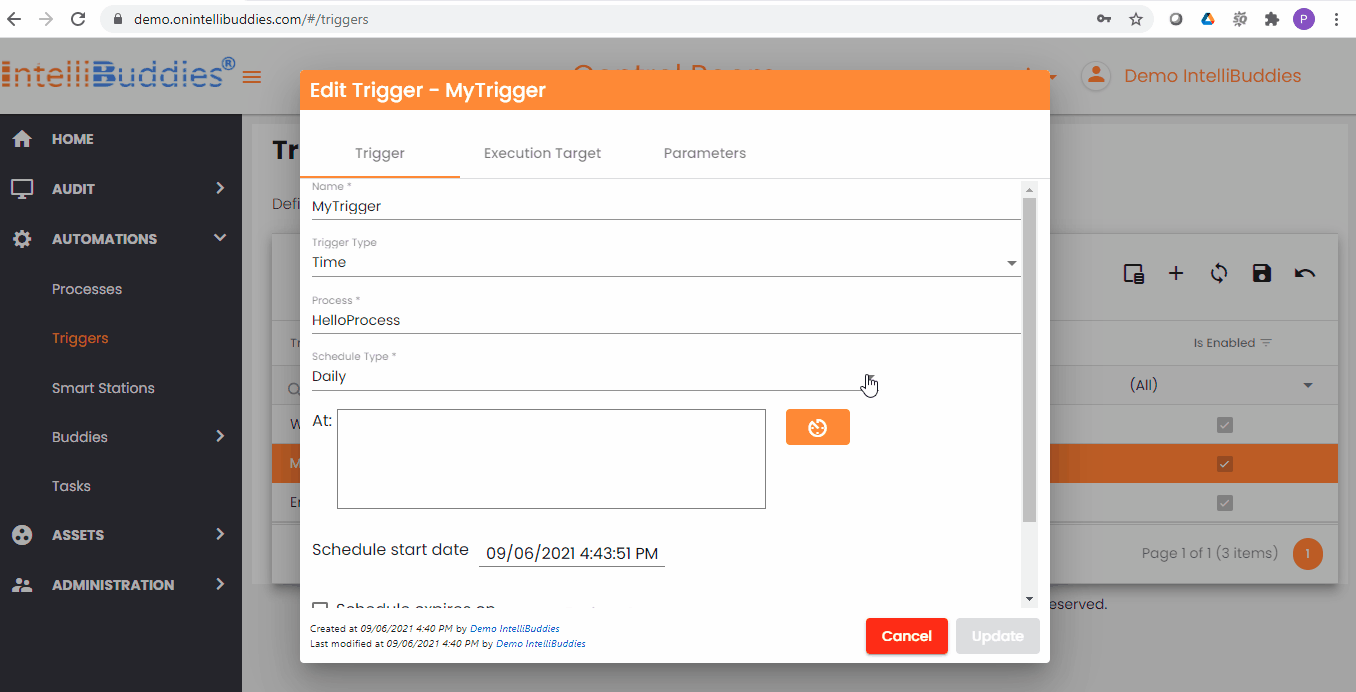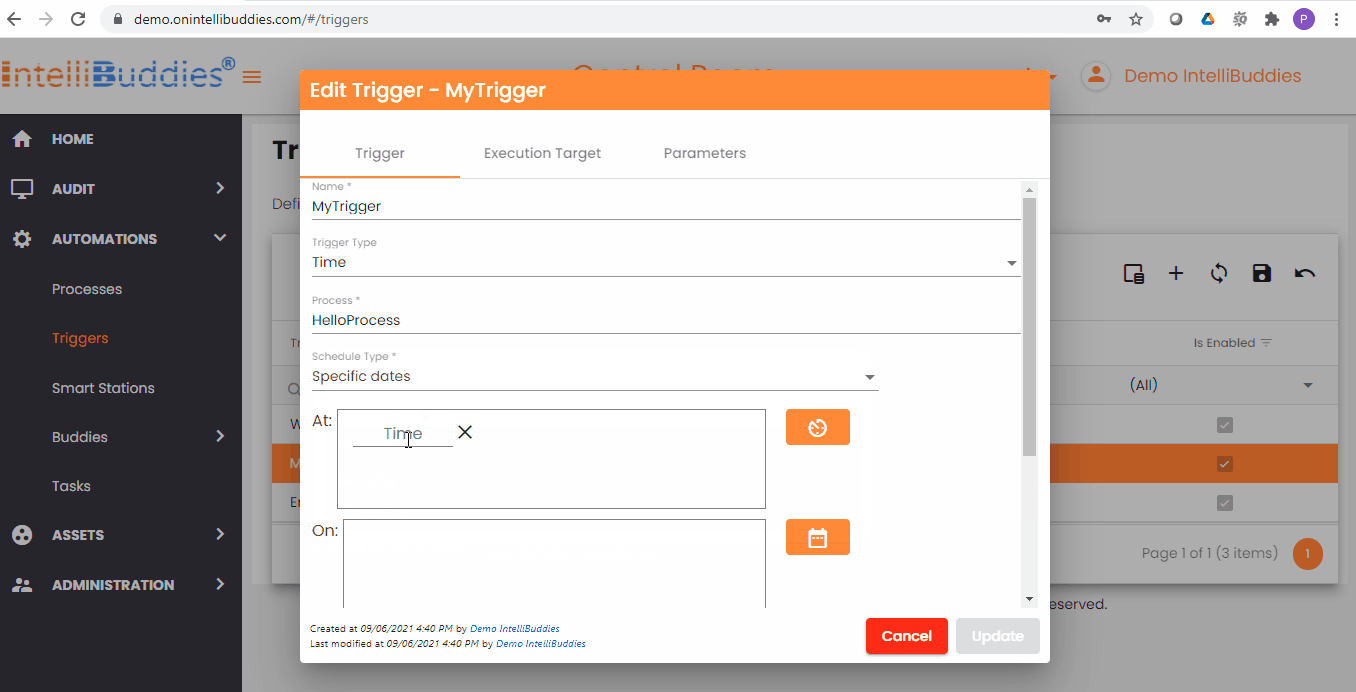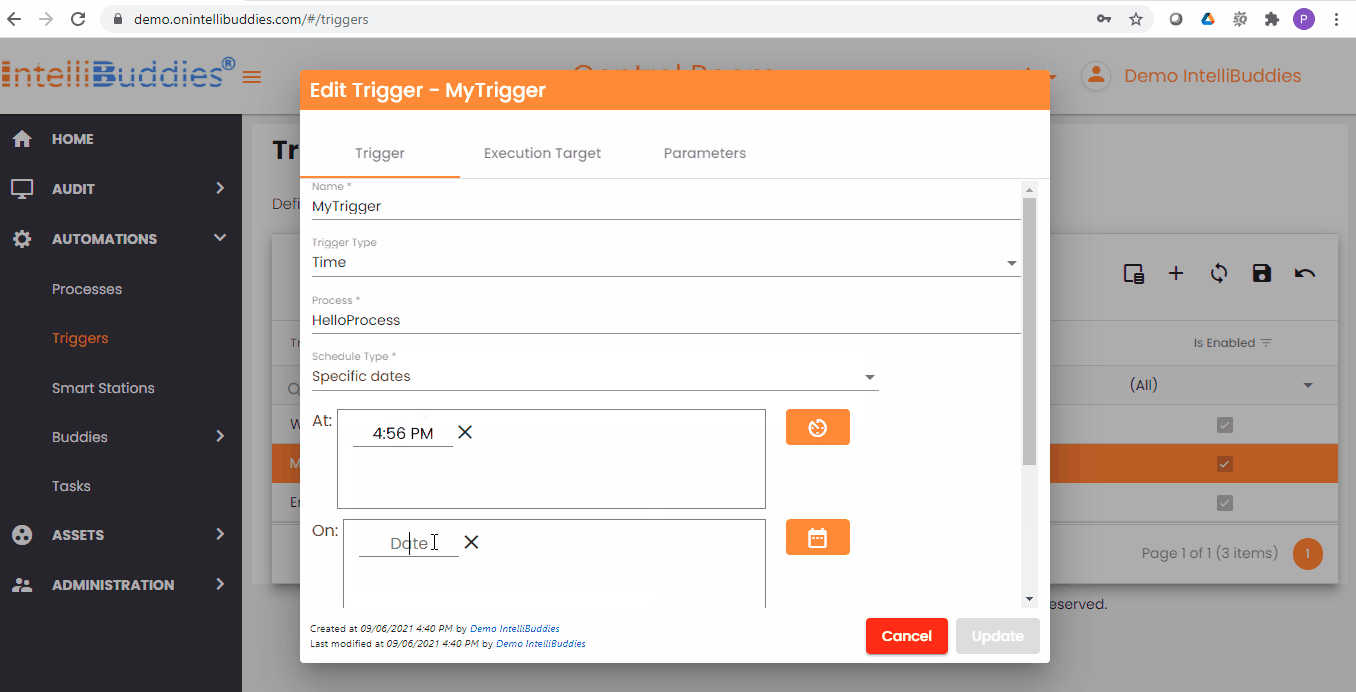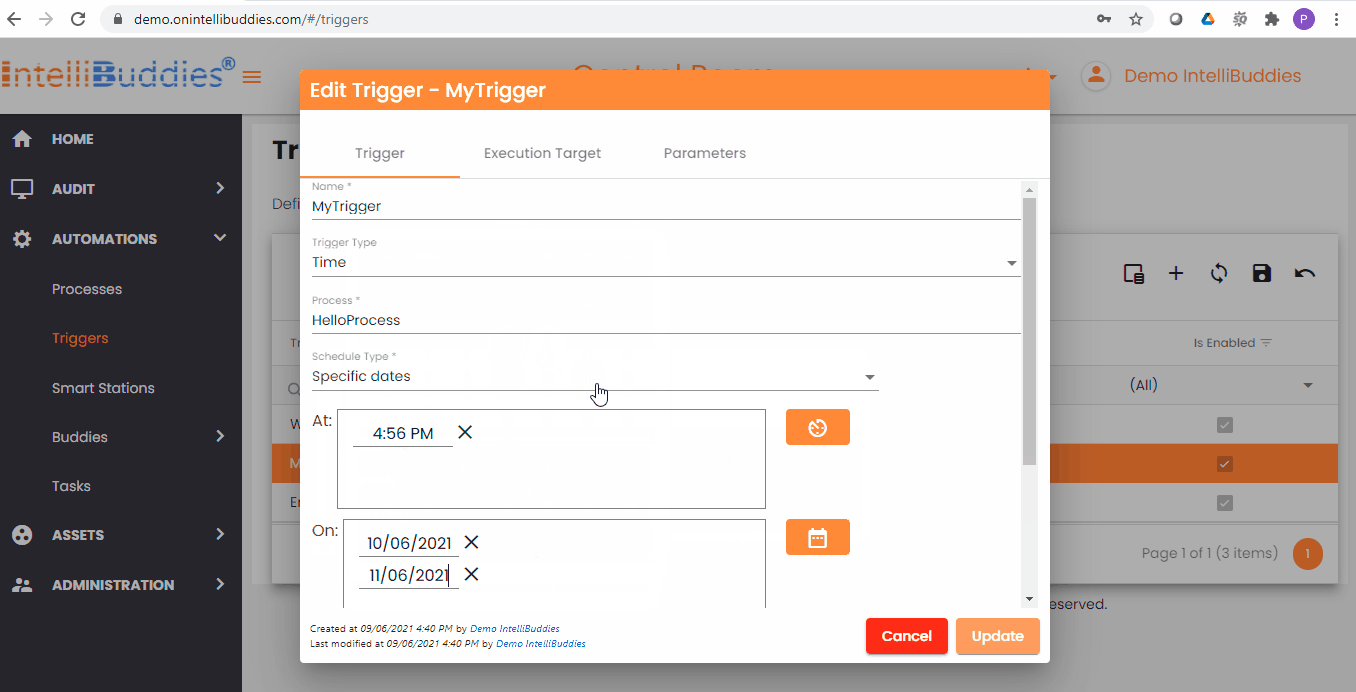
Time Trigger Criteria
You can specify your time trigger criteria by selecting the appropriate Schedule Types from the dropdown.
Schedule Types
| Schedule Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Daily | Use this schedule type to trigger a job execution on one or more specified schedule(s) daily |
| Specific Dates | Use this schedule type to trigger a job execution on one or more specified schedule(s) on all the date(s) specified. |
| Weekly | Use this schedule type to trigger a job on one or more specified schedule(s) on all the selected days of the week. |
| Monthly | Use this schedule type to trigger a job on one or more specified schedule(s) on all the selected day(s) of the week within the specified month(s) |
| Recurring | Use this schedule type to trigger a job repeatedly on the specified time interval |
Email Trigger Criteria
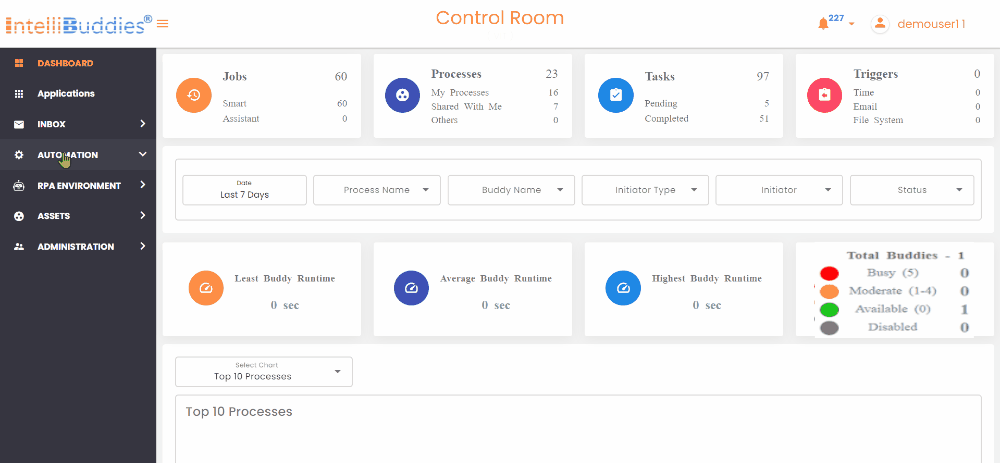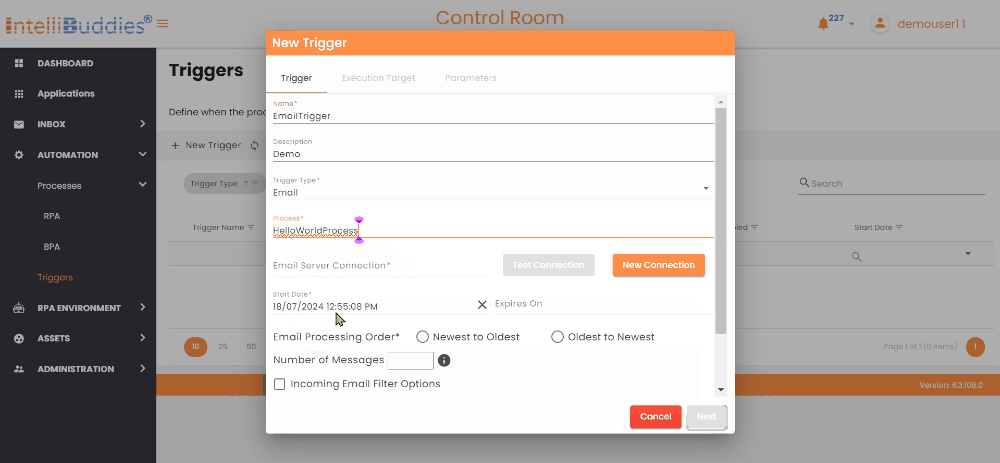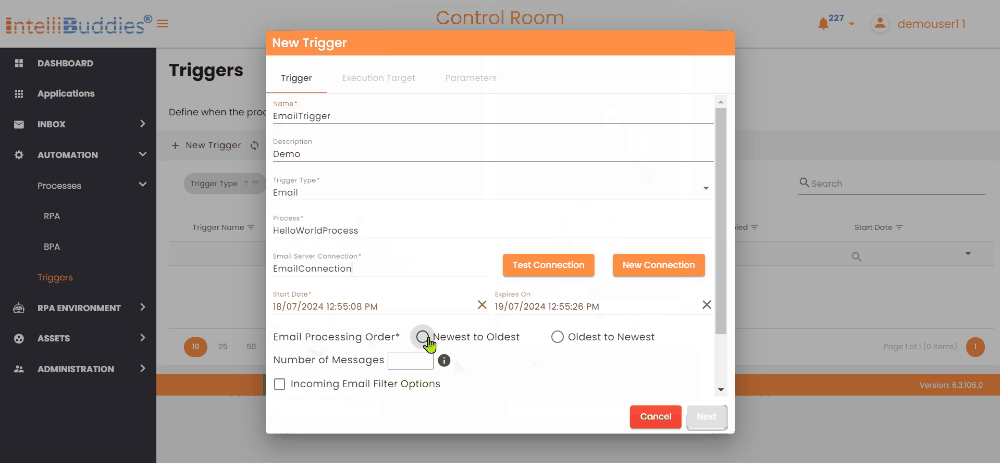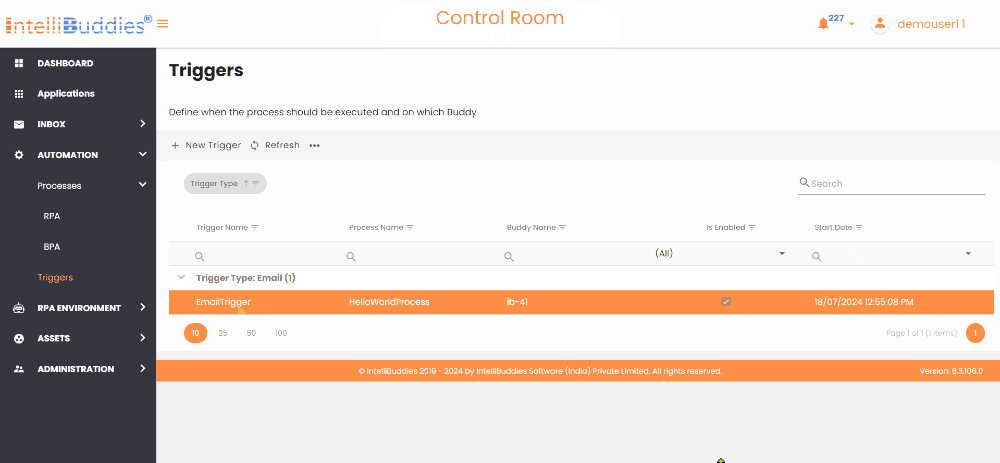
You can specify the email trigger criteria using the following fields.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Email Server Connection | Select a Connection from the available Email Server Connections. |
| Test Connection | Select this button to authenticate the credentials associated with the chosen connection. |
| New Connection | Click this button to create a new Email Server Connection. |
| Incoming Email Filter Options | Check this box to specify a Email Filter while fetching emails from the Server. |
| Number of Messages | Specify the count if you want to process only a specific number of emails. If not specified, all the unread emails which satisfy the filter condition will be processed. |
| Email Processing Order | Select the order you want to process emails. You can choose between Newest to Oldest to process the latest emails first or Oldest to Newest to process the oldest emails first. |
| Message Polling Interval | Specify the time interval in minutes to check emails on the Server. The limit is 10 minutes by default, but users can adjust it as needed. |
If you select POP3 as the Email Server Connection type, please review the limitation. It is recommended to consider more efficient alternatives for improved performance.
Email Filters
Using this multiple-filter option, users can apply filter criteria to extract the required emails. The user can also build the filter expressions.
Binding Email Trigger Parameters
Email Trigger provides runtime parameters that specify the trigger event details. These details are necessary for the process to handle its tasks. You can bind these runtime parameters to the corresponding input arguments of the process. Here is the List of runtime parameters provided by Email Trigger.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| $Email_Message | System.Net.MailMessage | The email message triggered this Process. You can access details such as sender, subject, received date, body text, attachments, and any other information from this parameter. |
Running Email Triggers on demand
You can run any Email Triggers on-demand to check for any new emails and to queue up the job on-demand by following the steps below:
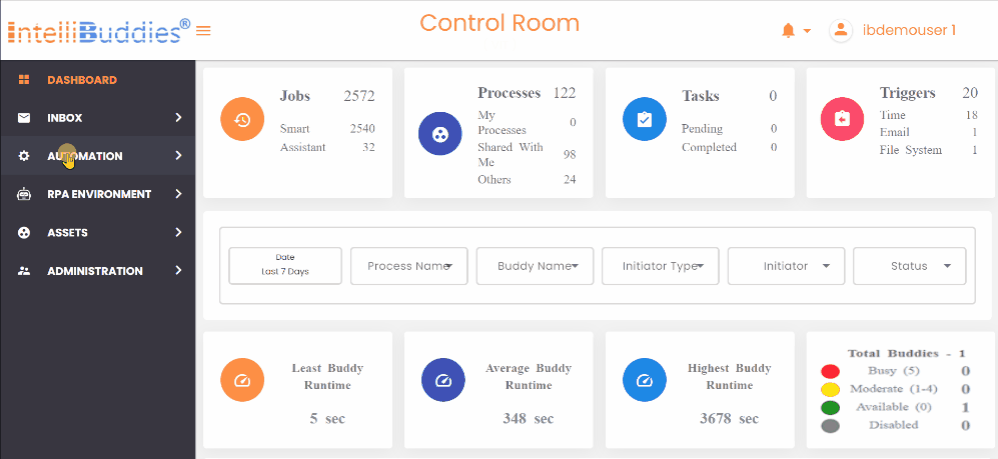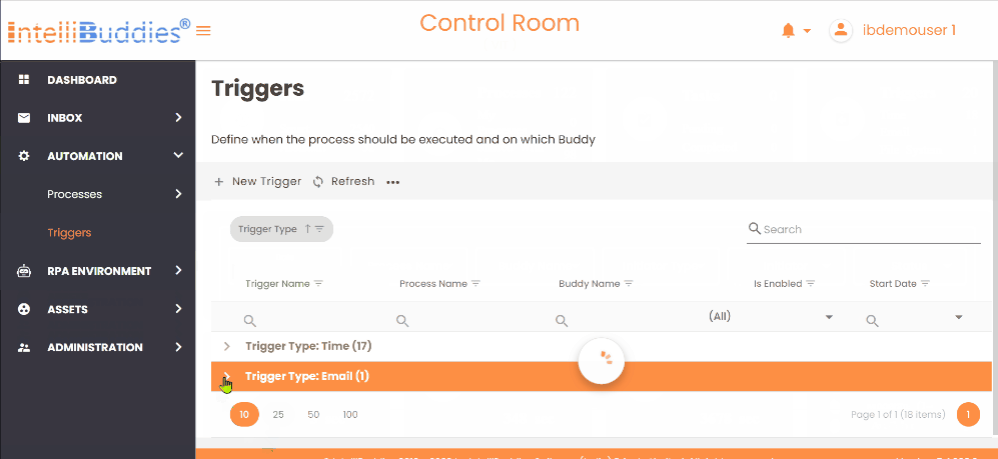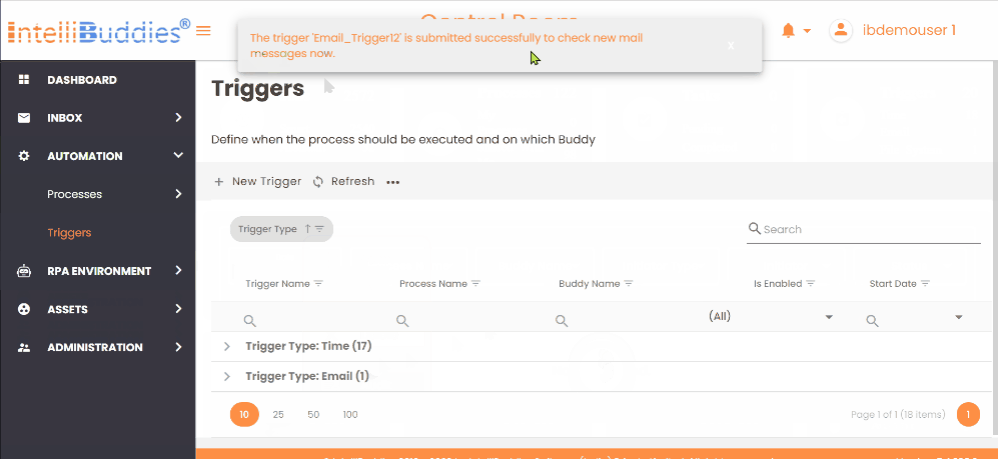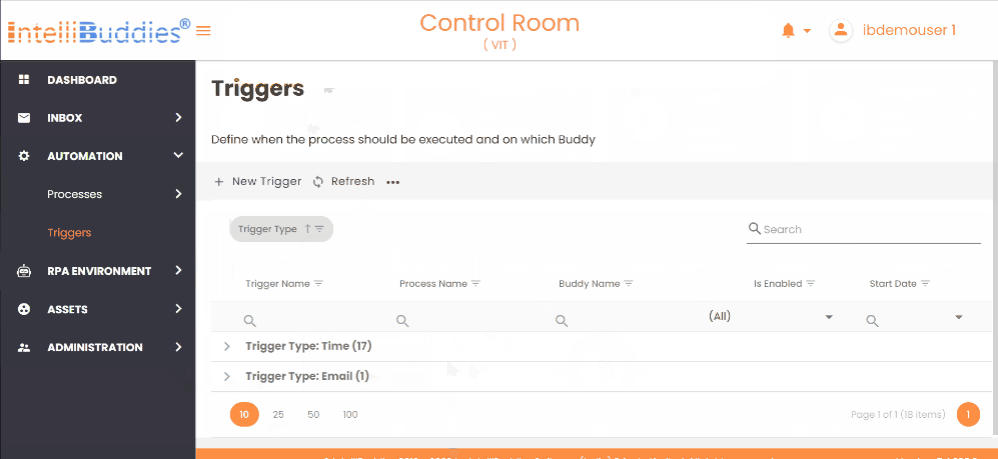
- Select an email trigger to run
- Select from Context-Menu > Run Now option.
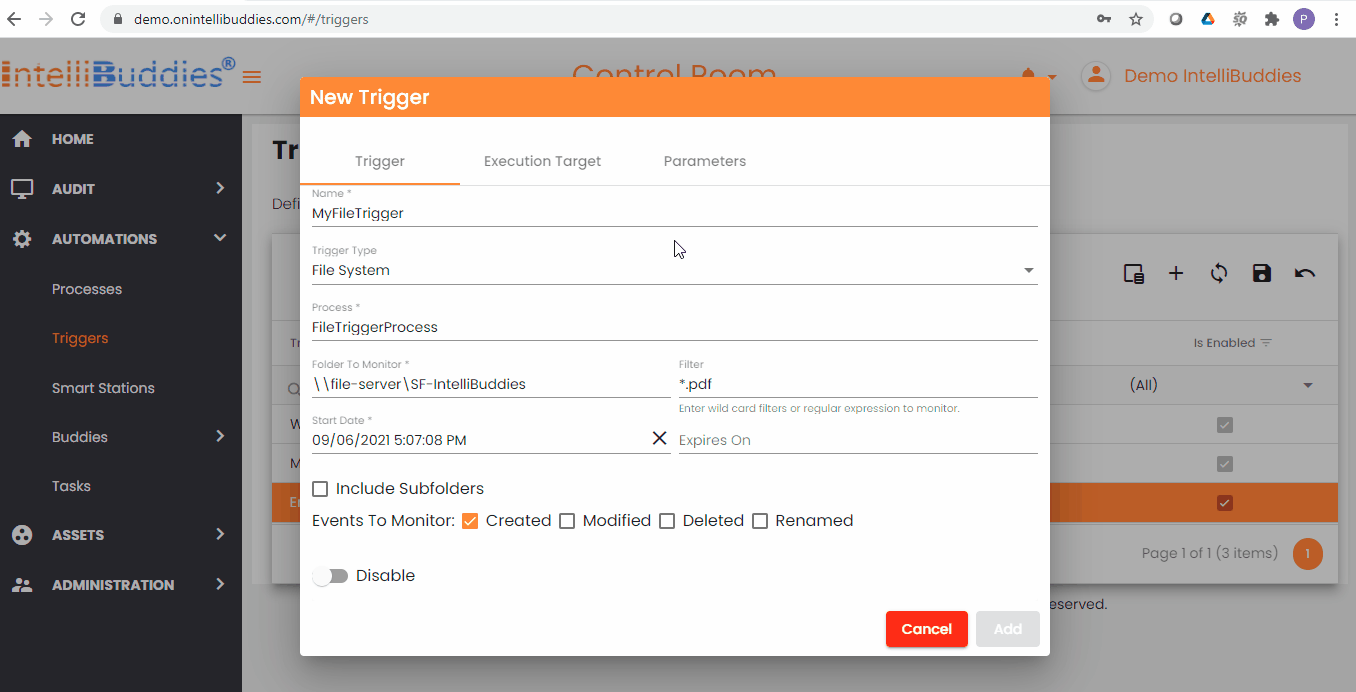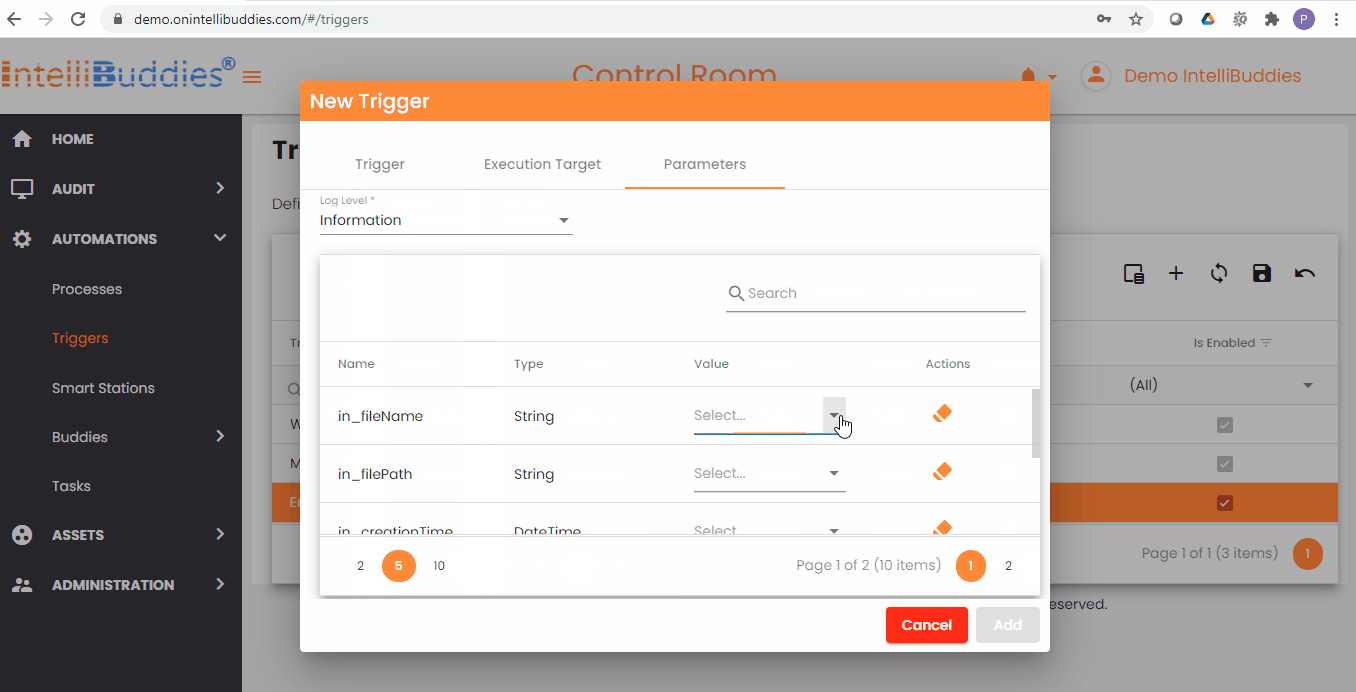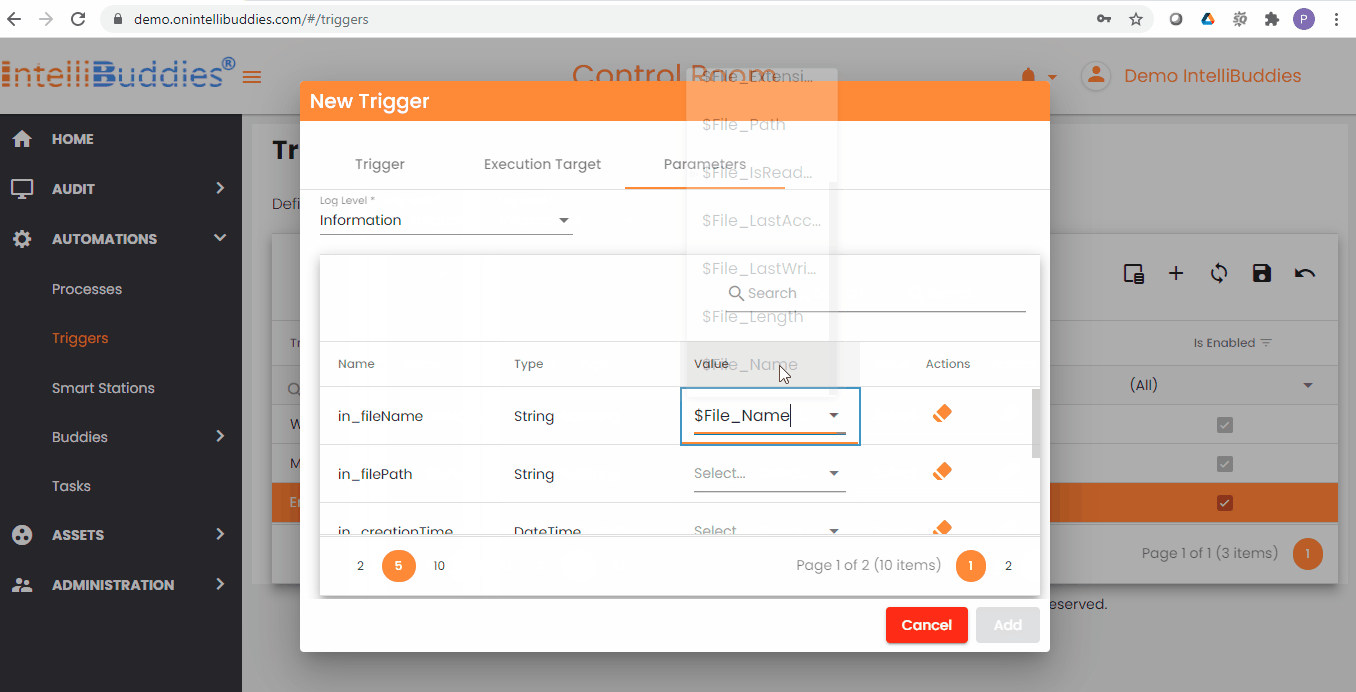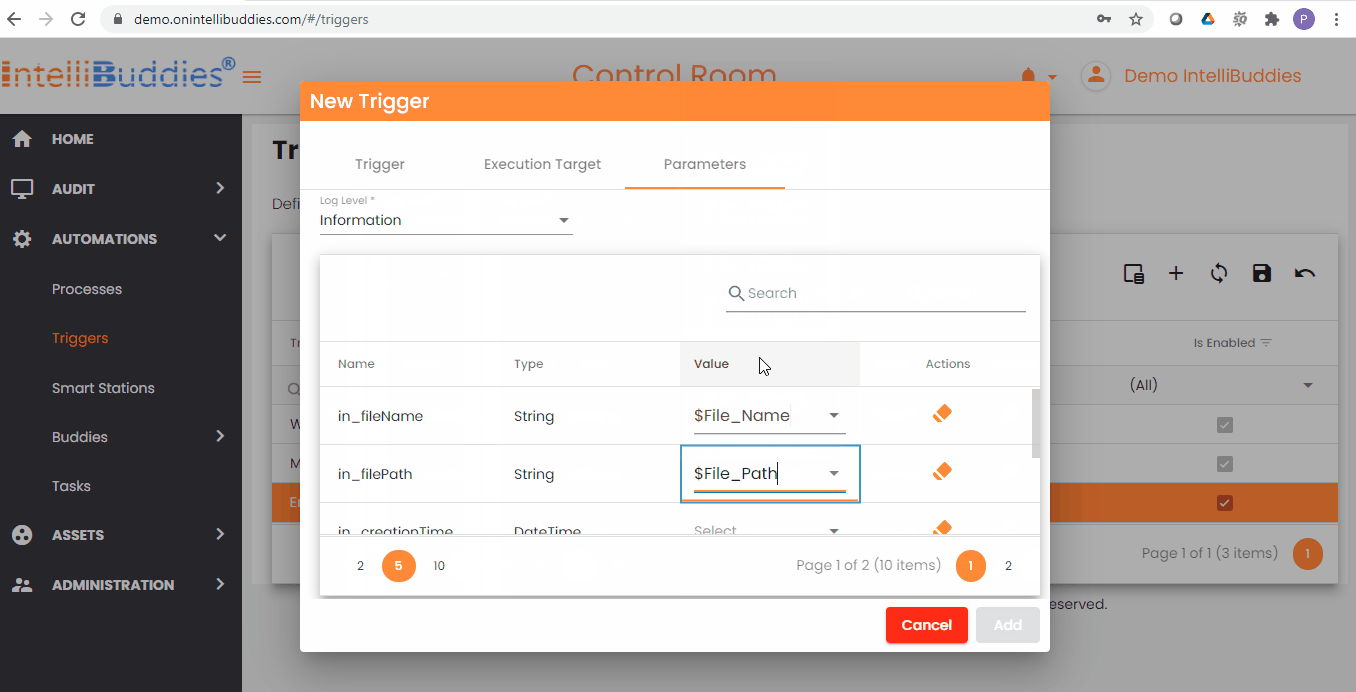
File System Trigger Criteria
You can specify the file system trigger criteria using the following fields.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| Folder To Monitor | Specify the folder to monitor. You can either specify the local file system path or the network path. For example: C:\MyMonitorFolder or \\file-server\MyMonitorFolder. Ensure that the monitored folder has the appropriate permissions. |
| Filter | You can specify the wildcard filter based on certain file types only if you want to trigger it. For example, specifying *.pdf here would trigger only when a PDF file is either Created/Modified/Deleted/Renamed under monitored folder(s) |
| Include Subfolders | Check this box if you want to monitor all the nested folders under the specified Folder To Monitor |
| Events To Monitor | Check the required events to monitor. You have the following options: |
Folder Permissions
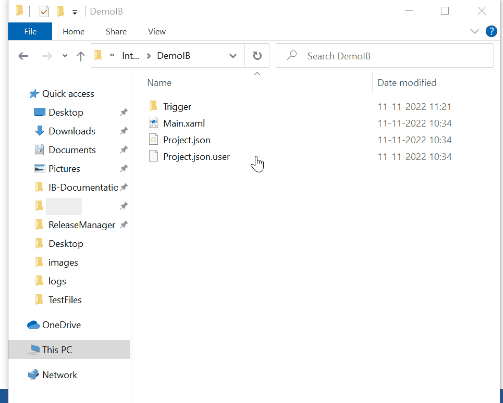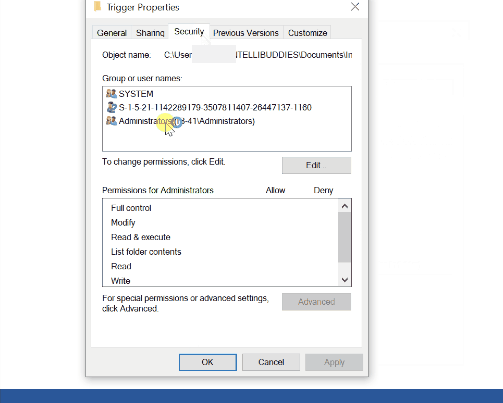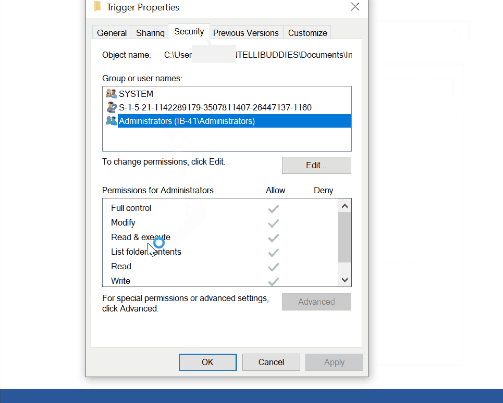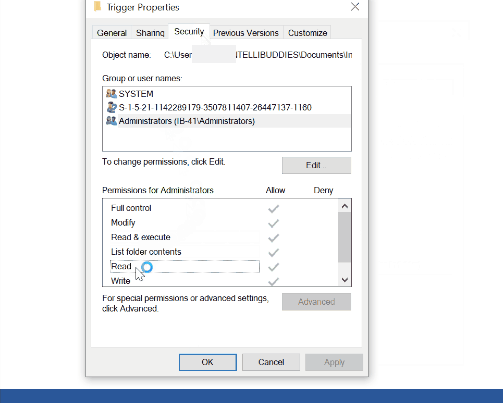
For a file system trigger to work, the monitored folder should have at least the following three permissions for user monitoring:
- read,
- read & execute
- list folder contents.
The user here refers to an App Pool Identity User or the Windows User based on how you have deployed your AI Command Center Server inside IIS. - If you configure AI Command Center Server to run under App Pool Identity inside IIS, the corresponding App Pool Identity account should have the appropriate permissions to the monitored folder.
- You can add the corresponding App Pool Identity account by prefixing the IIS AppPool domain before the account. For example, the default App Pool Identity account is represented as IIS AppPool\DefaultAppPool - This configuration will limit the usage of file system triggers to work only with local system folders.
- If you configure AI Command Center Server to run under a custom Windows User account inside IIS, the corresponding user should have the appropriate permissions to the monitored folder.
Locate the permissions by right-clicking on the trigger folder and choosing the properties. In the properties dialog, go to the Security tab. Provide the appropriate permission to the user.
It is advisable to configure the AI Command Center Server within IIS to operate under a custom network domain account. This setup enables the file system trigger to function seamlessly across local folders and network-shared drives.
Binding File System Trigger Parameters
File System Trigger provides runtime parameters that specify the trigger event details. These details are necessary for the process to handle its tasks. You can bind these runtime parameters to the process's corresponding input arguments.
Here is the List of runtime parameters provided by File System Trigger.
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| $File_EventType | System.IO.WatcherChangeTypes | Specifies the type of file event that triggered this process execution. It can be one of the following values
|
| $File_Name | System.String | Specifies the Name of the file along with the file extension |
| $File_Path | System.String | Specifies the full path, including the folder and file name with extension |
| $File_FolderPath | System.String | Specifies the folder path where the file resides |
| $File_Extension | System.String | Specifies the extension of the file |
| $File_Length | System.Double | Specifies the size of the file |
| $File_CreationTime | System.DateTime | Specifies the created date and Time of the file |
| $File_LastWriteTime | System.DateTime | Specifies the modified date and Time of the file |
| $File_LastAccessTime | System.DateTime | Specifies the last accessed date and Time of the file |
| $File_IsReadOnly | System.Boolean | Specifies whether the file is read-only or not. A value of true indicates the file is read-only. |
$File_CreationTime, $File_LastWriteTime, and $File_LastAccessTime store their DateTime values in UTC Standard format.
Converting from UTC: To convert UTC to a specified Timezone, use the TimeZoneInfo.ConvertTimeFromUtc static method.
Converting to UTC: To convert from another Timezone to UTC, use the static TimeZoneInfo.ConvertTimeToUtc method.
You can create the TimeZoneInfo with the help of the TimeZoneInfo.FindSystemTimeZoneById method, in which you need to specify the name of the time zone you want, such as India Standard Time.
List Trigger Criteria
To set your list trigger criteria, choose the fields listed below.
| Field | Description |
|---|---|
| List | Specify the List by its name. |
| Events To Monitor | Choose the event to use as a trigger for the job. You have the following options: |
| Apply Filters | Toggle or enable this to add a List Trigger Filter. |
Binding List Trigger Parameters
The List Trigger provides runtime parameters that contain essential details about the list item that triggered the event. These parameters allow you to dynamically pass contextual data from the triggered row into your automation process, enabling more accurate and responsive behavior. You can bind these runtime parameters to the corresponding input arguments of the process to ensure they react appropriately based on the type of event and the associated data.
Default Runtime Parameters
The following runtime parameters are automatically available when a List Trigger is activated:
| Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| $ListItem.EventType | string | Event for which trigger fired. |
| $ListItem | object | The full data of the list item involved. |
Supported Event Types
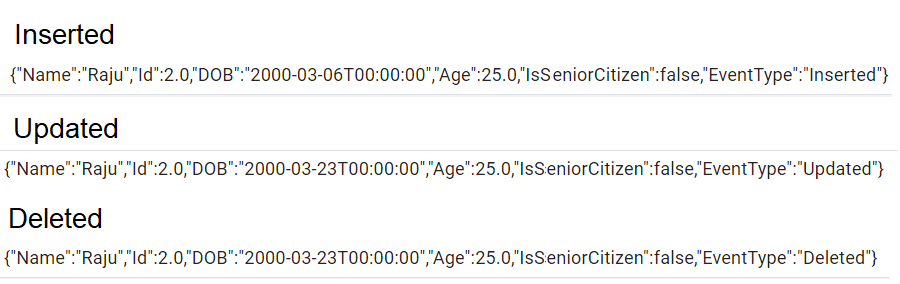
The List Trigger can respond to specific types of changes that occur in a list. These changes are categorized into three event types: Inserted, Updated, and Deleted. Each event type provides context for what action was performed on the list item, allowing your automation process to handle the event accordingly.
The table below describes each supported event type:
| Event Type | Description |
|---|---|
| Inserted | Triggered when you add a new item to the list. |
| Updated | Triggered when an existing item is modified. |
| Deleted | Triggered when you remove an item from the list. |
Usage With Example
-
Process Setup Create a process with the following input arguments:
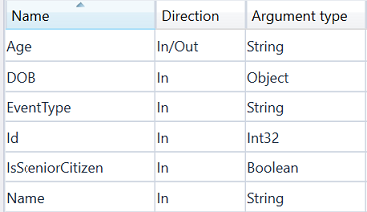
-
List Configuration Create a list with the following columns:
-
Trigger Configuration Configure a List Trigger to reference the above process and list. The runtime parameters from the list item were mapped to the corresponding process arguments as shown below:
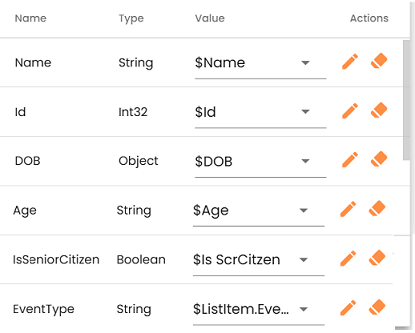
-
Trigger Execution When an item in the list is created, updated, or deleted, it fires the trigger and executes the process. The output appears as follows: