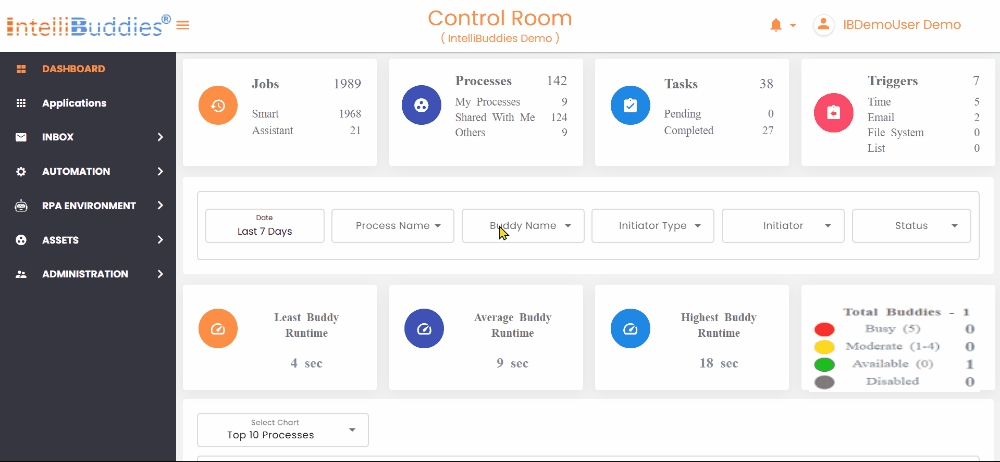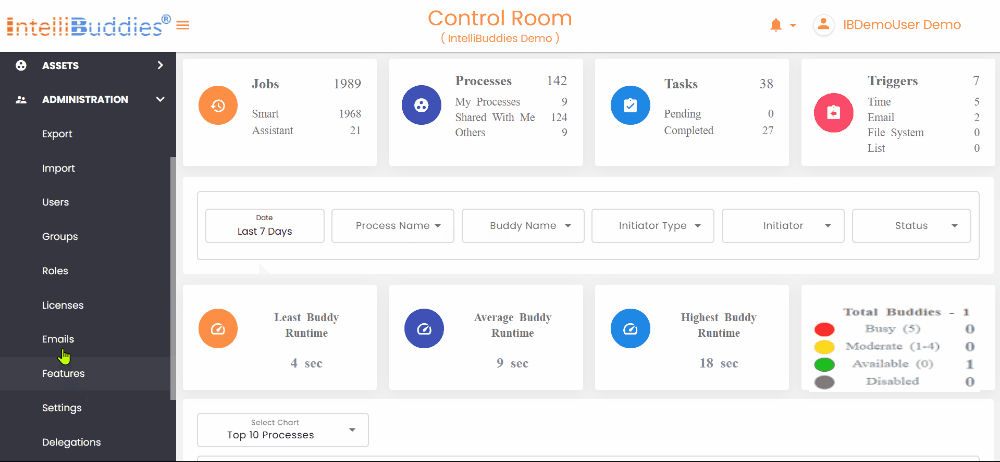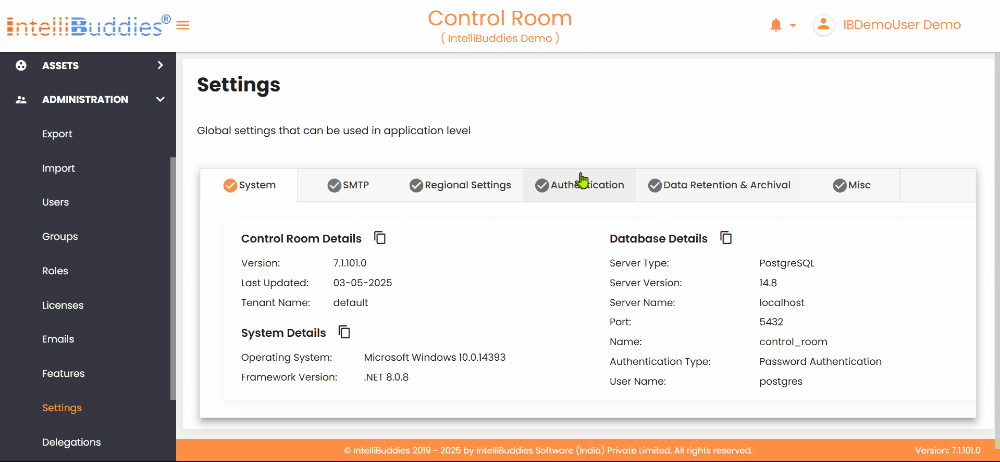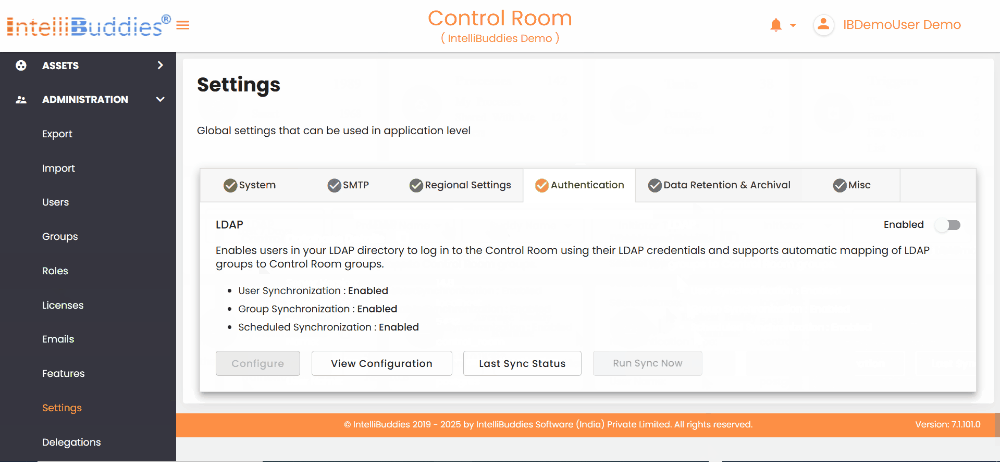
Microsoft Active Directory (LDAP)
Introduction
Use this guide to configure Microsoft Active Directory (AD) or a generic LDAP directory as an authentication provider for the AI Command Center.
You can configure any LDAP-based directory service, such as Microsoft Active Directory, OpenLDAP Directory, Apache Directory Server, or Apple Directory Server. You can set LDAP synchronization to automatically import users and groups from your Active Directory. By default, it assigns the RPA Member and BPA Member roles to newly created LDAP users.
Overview
Using LDAP authentication, you can:
- Register multiple LDAP providers (Microsoft AD or generic LDAP)
- Enable/Disable without losing configuration
- Synchronize users and groups on a schedule
Configuration flow
1) Basic Information
Provide basic details to identify and manage the provider:
- Provider Name – Enter a unique name for this configuration
- Description – Enter the brief description of the AD configuration.
- Enabled – Turn the provider on or off without deleting its configuration
2) LDAP Server Settings
Configure the LDAP server connection details:
| Setting | Description |
|---|---|
| Server Type | Select the type of LDAP server Microsoft Active Directory and LDAP. If you use Microsoft Active Directory, choose that option; for other LDAP servers, select LDAP from the dropdown. |
| Enable Single Sign On | Selecting Microsoft Active Directory provides an additional option to enable Single Sign-On (SSO). |
| Host | Specify the LDAP server name or IP address. |
| Port | Specify the port. By default, set to 389 |
| Use SSL-secured connection | If SSL is enabled, select this option to ensure secure data transmission between your browser and the server, protecting against unauthorized access. |
| User Name | Specify the username to retrieve details of domains, organizational units, groups, and users. You can also enter the distinguished name of the user, e.g., CN=admin, CN=Users, DC=TestDomain, DC=com. |
| Password | Specify password |
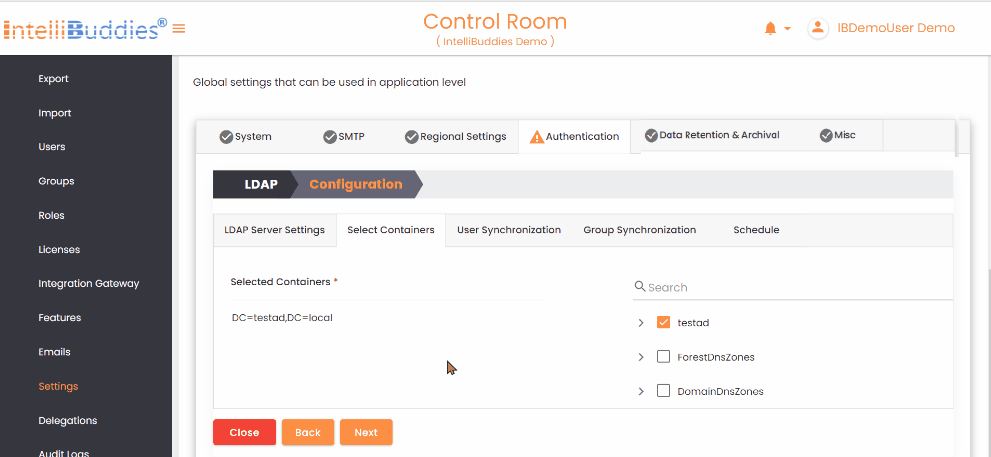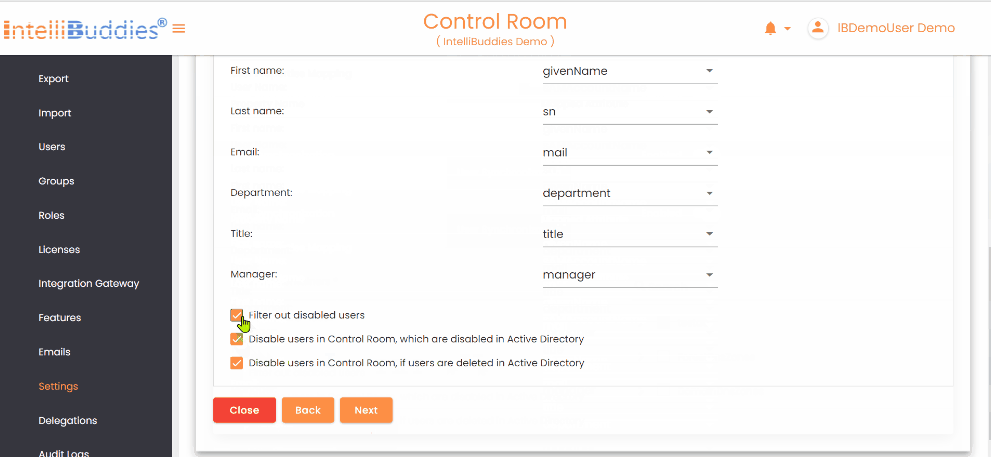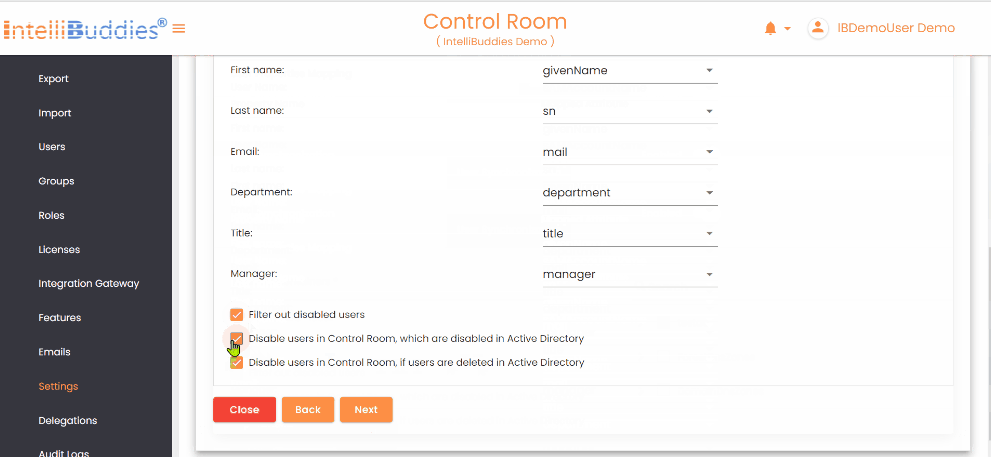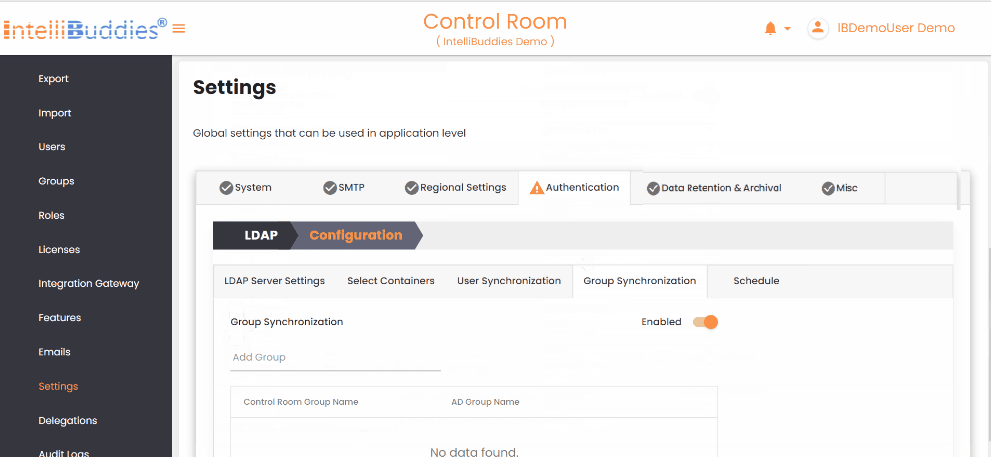
3) Select Containers
Browse the directory structure and select the organizational units (OUs) that define the scope of user and group synchronization.
4) User Synchronization
Configure how users synchronize from the directory into the AI Command Center:
- Map user attributes such as: - Account name - First/Last name - Email - Department - Title - Manager
- Defaults are suggested automatically; adjust only for custom attributes
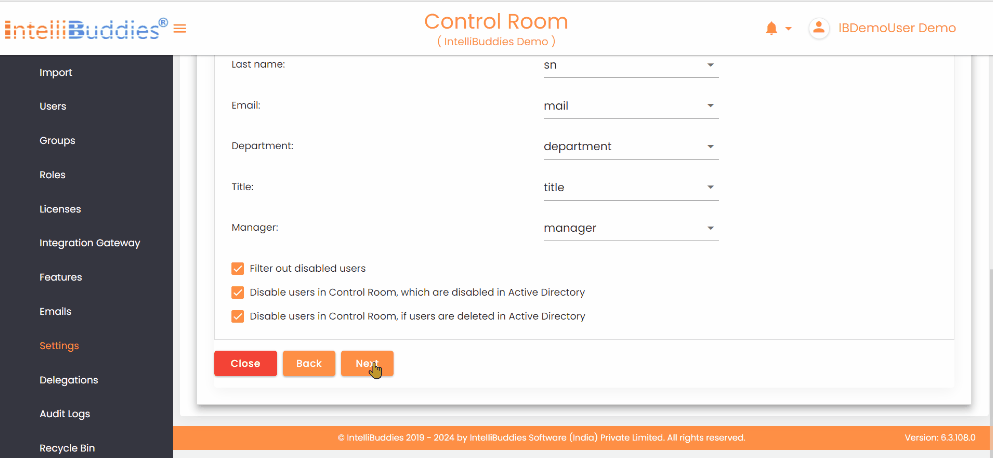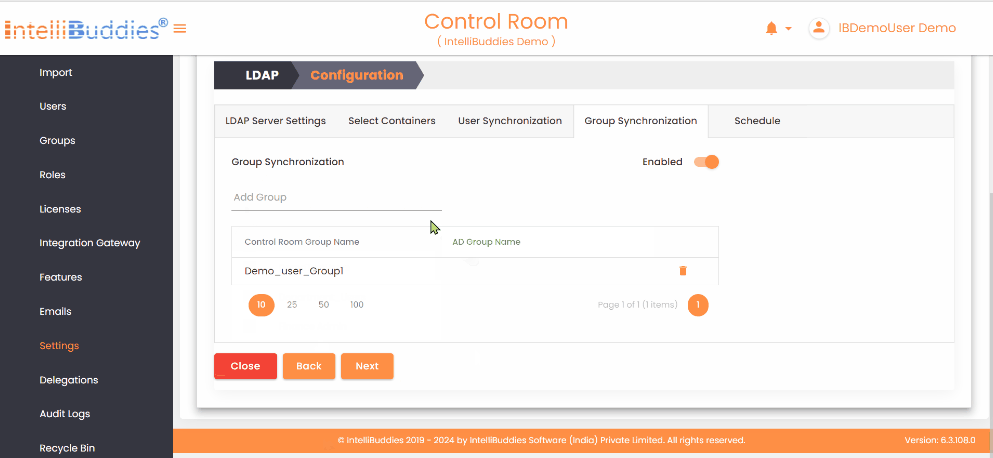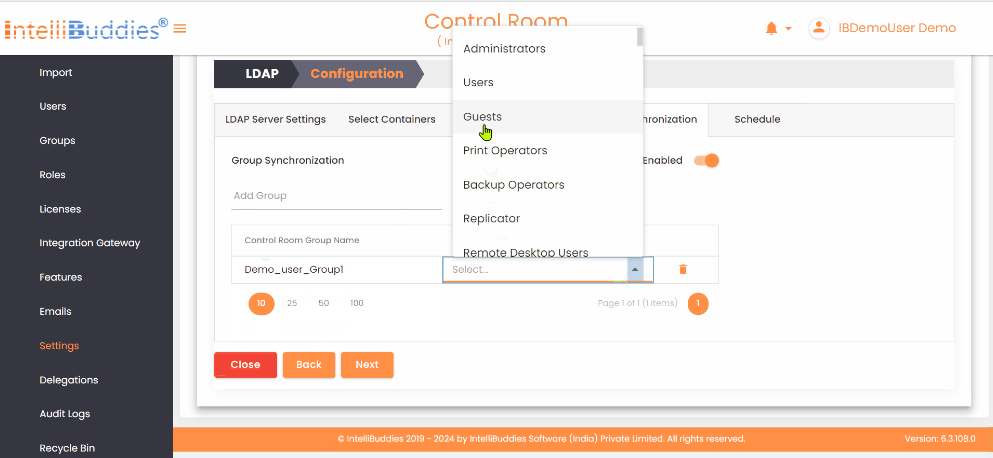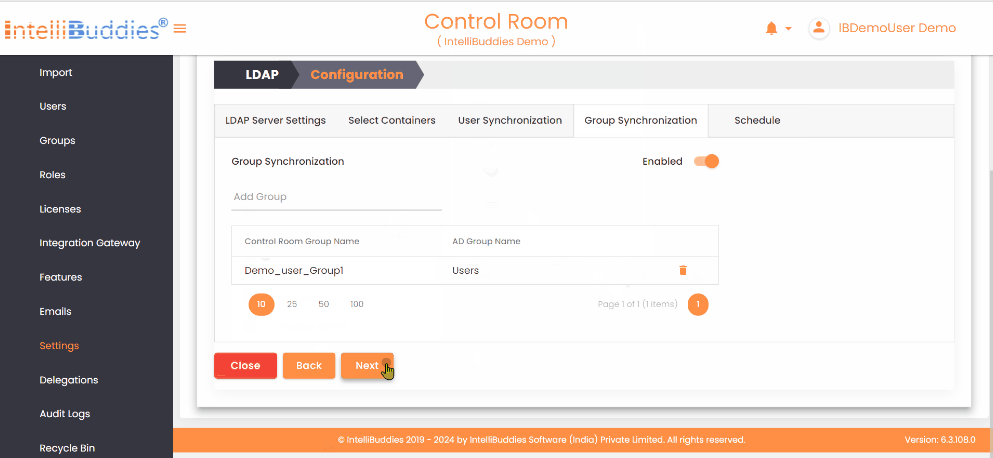
- Configure synchronization options: - Filter out disabled users - Disable the AI Command Center user when the AD user is disabled - Disable the AI Command Center user when the AD user is deleted
- Specify Notify To email addresses for synchronization error notifications
Ensure the user has Read, List Content, and Search permissions on the schema to retrieve attributes successfully.
| Options | Description |
|---|---|
Filter out disabled users | Check this option to exclude disabled users from Active Directory during synchronization. |
Disable users in Control Room, which are disabled in Active Directory | Check this option to automatically disable AI Command Center users when they are disabled in Active Directory |
Disable users in Control Room, if users are deleted in Active Directory | Check this option to automatically disable AI Command Center users when they are deleted from Active Directory. |
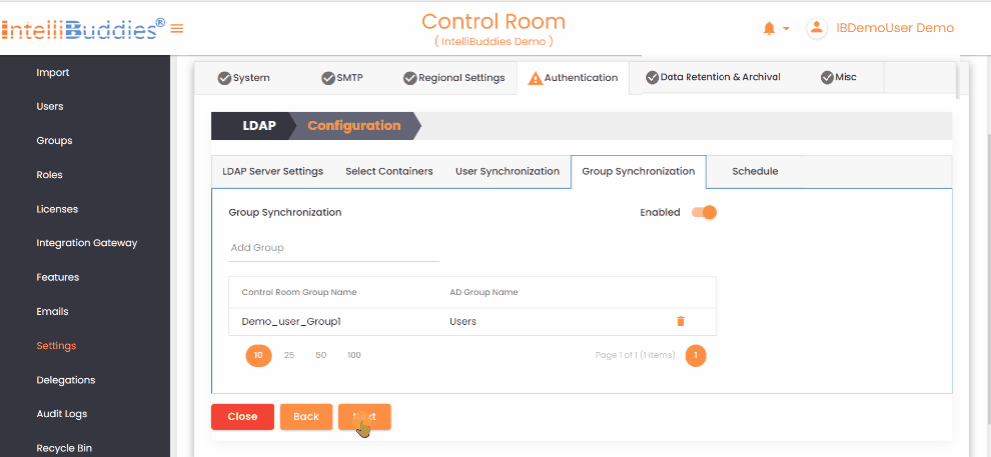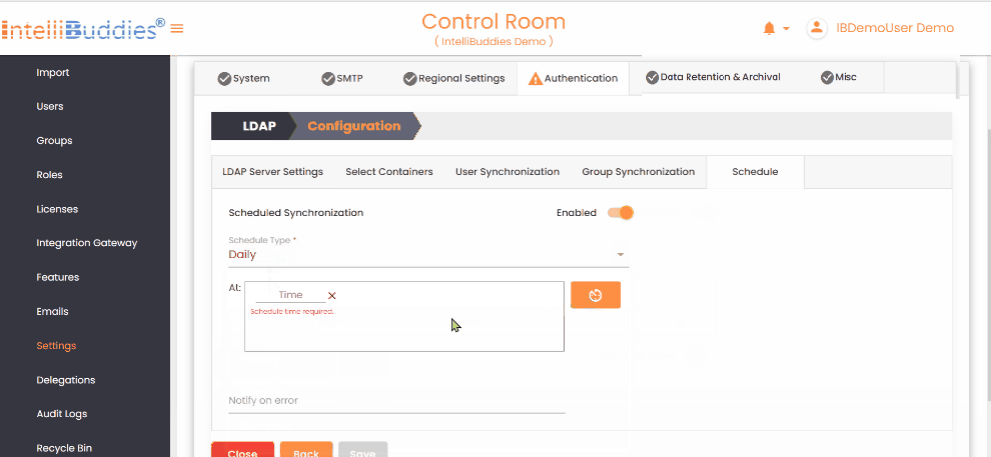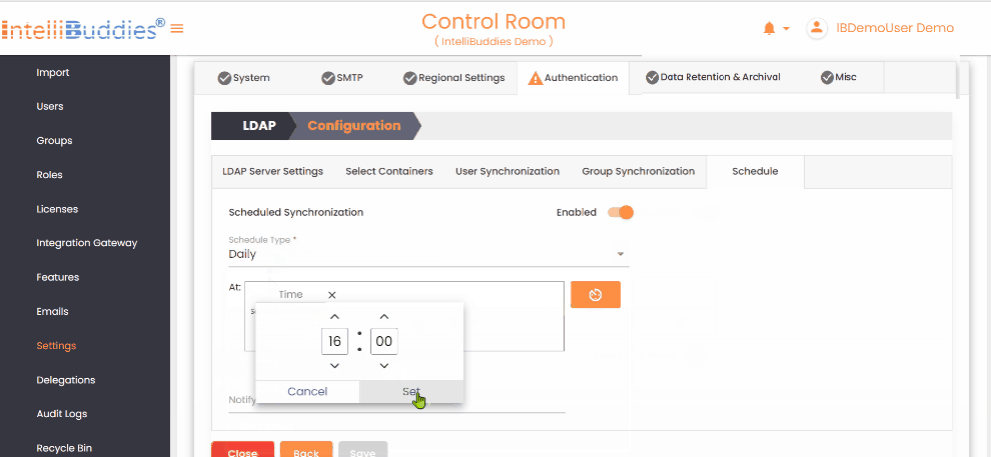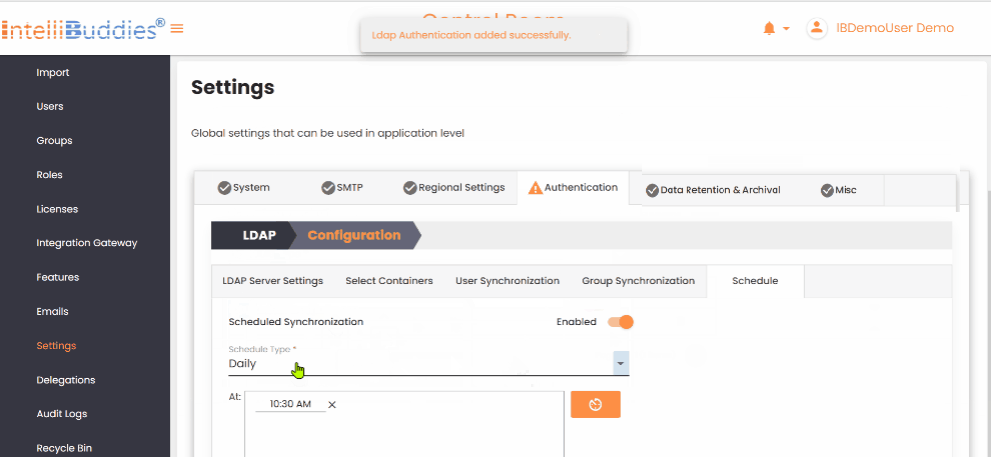
4) Group Synchronization
To synchronize groups:
- Create the required groups in the AI Command Center.
- Map each AI Command Center group to its corresponding Active Directory group in the Group Synchronization tab.
The system synchronizes only mapped groups and reflects Active Directory membership changes in the corresponding AI Command Center groups.
5) Set up periodic user and group synchronization in the Schedule tab.
- Use appropriate Schedule Types
6) Review & Save
Review the configuration and save your changes:
- The system creates or updates the provider configuration.
- Existing passwords remain unchanged unless you explicitly update them.
After synchronizing users from Active Directory, users can sign in using their AD credentials and set a password. Once a password is set, users can authenticate using either Basic Authentication or LDAP Authentication. If Single Sign-On (SSO) is enabled, users can sign in seamlessly using their Active Directory credentials.